随着矿产资源开采难度的日益加大,工艺矿物学在矿产开发过程中的重要作用越来越凸显[1,2,3,4]。通过检测矿石性质,明确影响选冶指标的主要因素,能够为优化选冶工艺指标提供依据[5,6,7,8,9,10,11]。某金矿采用两段一闭路破碎、一段磨矿、一次粗选、两次精选、两次扫选、再磨后氰化浸出及锌粉置换获得合质金的工艺流程。在生产过程中发现金的浸出率一直较低,为了查明导致金回收率难以提高的原因,利用北京矿冶研究总院研发的工艺矿物学自动测试系统BPMA(电子探针)对该矿石开展了工艺矿物学研究。BPMA系统通过背散射电子图像处理技术实现了矿物颗粒的精准分离,通过被检测矿物的能谱分析结果与相应矿物理论合成能谱模式的比对,进行矿物的成分分析与识别,并结合分析软件得出矿物的各种工艺矿物学参数,可为优化选冶工艺指标提供依据[12,13,14,15]。
1 矿石特征
1.1 矿石成分分析
矿样为某含金原生矿石,对矿样进行了化学多元素成分分析,结果表明,矿石金含量较高,为5.36×10-6(表1)。由于碳对金的回收有较大影响,对碳进行了物相分析,结果表明,矿石中的碳绝大部分是以碳酸盐的形式存在(矿石中碳酸盐质量分数为4.0%,其中碳酸盐中的碳占总碳量的96.15%),对金的回收影响较小,故不进行碳的系统分析。
表1 矿石化学成分分析结果
Table 1
| 元素 | 质量分数/% | 元素 | 质量分数/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Au* | 5.36 | Ca | 13.15 |
| Ag* | 3.92 | Fe | 15.89 |
| C | 4.16 | Al | 1.23 |
| Mg | 0.44 | As | 1.56 |
| Si | 12.62 | Pb | 0.40 |
| S | 12.78 |
1.2 矿石中金的赋存状态
表2 矿石中金的赋存状态分析结果
Table 2
| 物相类别 | 质量分数/(×10-6) | 分布率/% |
|---|---|---|
| 合计 | 5.36 | 100.00 |
| 自然金中的金 | 4.85 | 90.48 |
| 银金矿中的金 | 0.51 | 9.52 |
1.3 矿石矿物组成
经扫描电镜及能谱等分析,该样品中的主要金矿物是自然金和银金矿;金属矿物主要有黄铁矿、磁铁矿和毒砂等;脉石矿物主要有方解石、石英、云母类和白云石类等(表3)。
表3 矿石的矿物组成及相对含量
Table 3
| 矿物类型 | 质量分数/% | |
|---|---|---|
| 合计 | 100.00 | |
| 金属矿物 | 铁矿 | 21.93 |
| 毒砂 | 3.47 | |
| 磁铁矿 | 3.57 | |
| 磁黄铁矿 | 0.78 | |
| 其他 | 1.02 | |
| 小计 | 30.77 | |
| 脉石矿物 | 方解石 | 30.68 |
| 石英 | 22.78 | |
| 云母类 | 7.34 | |
| 白云石类 | 3.97 | |
| 其他 | 4.46 | |
| 小计 | 69.23 | |
2 含金矿物嵌布特征
本文中的金矿物是基于自然金(金质量分数在80%以上、银质量分数在20%以下)、银金矿(金质量分数在50%~80%之间、银质量分数在20%~50%之间)、银金矿(银质量分数在50%~80%之间、金质量分数在20%~50%之间)和自然银(银质量分数在80%以上、金质量分数在20%以下)的标准进行分类的。
2.1 自然金
自然金是样品中的主要含金矿物之一,其含金量占金总量的90.48%。样品中自然金能谱定量分析结果见表4。
表4 自然金能谱定量分析结果
Table 4
| 序号 | 元素质量分数/% | 序号 | 元素质量分数/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au | Ag | Au | Ag | ||
| 1 | 84.16 | 15.84 | 17 | 98.89 | 1.11 |
| 2 | 91.42 | 8.58 | 18 | 88.54 | 11.46 |
| 3 | 86.40 | 13.60 | 19 | 84.97 | 15.03 |
| 4 | 80.27 | 19.73 | 20 | 84.43 | 15.57 |
| 5 | 85.90 | 14.10 | 21 | 87.84 | 12.16 |
| 6 | 87.04 | 12.96 | 22 | 87.51 | 12.49 |
| 7 | 90.81 | 9.19 | 23 | 99.67 | 0.33 |
| 8 | 84.04 | 15.96 | 24 | 84.33 | 15.67 |
| 9 | 97.36 | 2.64 | 25 | 82.96 | 17.04 |
| 10 | 85.20 | 14.80 | 26 | 92.39 | 7.61 |
| 11 | 83.31 | 16.69 | 27 | 89.19 | 10.81 |
| 12 | 80.61 | 19.39 | 28 | 95.29 | 4.71 |
| 13 | 84.34 | 15.66 | 29 | 80.22 | 19.78 |
| 14 | 95.99 | 4.01 | 30 | 90.16 | 9.84 |
| 15 | 82.91 | 17.09 | 31 | 99.00 | 1.00 |
| 16 | 99.79 | 0.21 | |||
从表4可以得出,样品中自然金的金平均质量分数为86.49%,银平均质量分数为13.51%。
自然金平均粒径为3.06 μm,其中最大颗粒粒度为16.40 μm×13.60 μm,其他颗粒的粒度均小于10 μm,呈细粒—微细粒嵌布。具体粒度分布统计结果见表5。
表5 自然金粒度嵌布统计结果
Table 5
| 粒级/μm | 自然金 | |
|---|---|---|
| 质量分数/% | 累积量/% | |
| -20+10 | 54.63 | 54.63 |
| -10+4 | 8.02 | 62.65 |
| -4+3 | 20.59 | 83.25 |
| -3+2 | 11.00 | 94.25 |
| -2+1 | 5.34 | 99.59 |
| -1 | 0.41 | 100.00 |
在矿石粒度为-200目含量占70%的情况下,自然金单体解离度仅为2.15%,金主要与毒砂、黄铁矿连生。
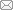
图1
图1
自然金的主要嵌布状态
(a)矿石中的自然金与黄铁矿紧密连生;(b)矿石中与毒砂连生的自然金被黄铁矿包裹
Fig.1
Main embedding state of natural gold
2.2 银金矿
银金矿是矿石中主要的金矿物之一。对样品中的银金矿进行能谱定量分析,结果表明,样品中银金矿金平均质量分数为76.37%,银平均质量分数为23.63%(表6)。
表6 银金矿能谱定量分析结果
Table 6
| 序号 | 元素质量分数/% | 序号 | 元素质量分数/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au | Ag | Au | Ag | ||
| 1 | 77.19 | 22.81 | 6 | 73.85 | 26.15 |
| 2 | 77.70 | 22.30 | 7 | 75.55 | 24.45 |
| 3 | 76.48 | 23.52 | 8 | 75.74 | 24.26 |
| 4 | 74.39 | 25.61 | 9 | 78.57 | 21.43 |
| 5 | 78.12 | 21.88 | 10 | 78.51 | 21.49 |
银金矿平均粒径为2.16 μm,其中最大颗粒粒度为5.5 μm×2.4 μm,其他颗粒粒度均小于10 μm,呈细粒—微细粒嵌布。具体粒度分布情况见表7。
表7 银金矿粒度嵌布统计结果
Table 7
| 粒级/μm | 银金矿 | |
|---|---|---|
| 相对含量/% | 累积量/% | |
| -10+4 | 26.12 | 26.12 |
| -4+3 | 44.59 | 70.71 |
| -3+2 | 20.02 | 90.73 |
| -2+1 | 8.76 | 99.49 |
| -1 | 0.51 | 100.00 |
通过研究发现,单体解离的银金矿占1.60%,解离度在80%~100%之间的连生体占73.96%,其他程度的银金矿占24.44%,可见,该矿石中的银金矿主要以连生体形式存在。银金矿主要与黄铁矿、毒砂等矿物连生,其中与毒砂连生的银金矿含量为21.71%,与黄铁矿连生的银金矿含量为65.23%,与其他矿物连生的银金矿含量为10.91%。银金矿的主要嵌布状态见图2。
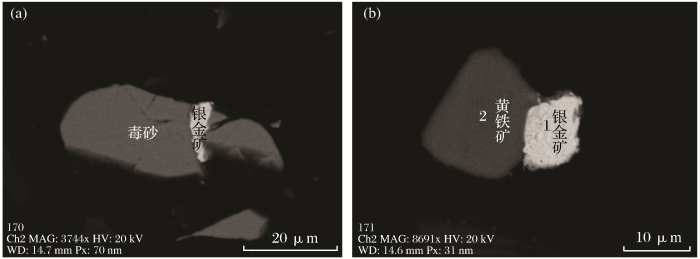
图2
图2
银金矿的主要嵌布状态
(a)矿石中的银金矿嵌布在毒砂裂隙中;(b)矿石中的银金矿与黄铁矿连生
Fig.2
Main embedding state of silver gold mine
2.3 金矿物的嵌布状态
矿石中主要含金矿物有自然金和银金矿,回收金主要是回收自然金和银金矿中的金。研究发现,矿石中的金主要以连生金的形式存在,占70.60%,其次为包裹金,占24.63%,粒间金和单体金均很少。含金矿物嵌布状态统计结果见表8。
表8 含金矿物嵌布状态统计结果
Table 8
| 赋存类别 | 赋存状态 | 相对含量/% |
|---|---|---|
| 合计 | 100.00 | |
| 包裹金 | 脉石包裹 | 0.80 |
| 金属矿物包裹 | 23.83 | |
| 晶间金 | 脉石粒间 | 0.35 |
| 金属矿物粒间 | 2.31 | |
| 连生金 | 脉石裂隙 | 3.29 |
| 金属矿物裂隙 | 67.31 | |
| 单体金 | - | 2.11 |
3 载金矿物的嵌布特征
黄铁矿和毒砂是矿石中金的主要载体矿物,其嵌布特征如下所述。
3.1 黄铁矿
表9 矿石中黄铁矿粒度分布统计结果
Table 9
| 粒级/μm | 黄铁矿 | |
|---|---|---|
| 相对含量/% | 正累积含量/% | |
| +74 | 1.73 | 1.73 |
| -74+53 | 5.65 | 7.38 |
| -53+43 | 7.58 | 14.97 |
| -43+38 | 6.94 | 21.90 |
| -38+20 | 36.70 | 58.60 |
| -20+15 | 11.35 | 69.95 |
| -15+10 | 11.50 | 81.45 |
| -10+5 | 10.46 | 91.91 |
| -5 | 8.09 | 100.00 |
单体解离的黄铁矿占45.87%,解离度在80%~100%之间的连生体占46.59%,其他解离程度的黄铁矿占7.54%,可知样品中的黄铁矿主要以单体和连生体形式存在,其中连生状态的黄铁矿主要与石英和毒砂连生,少量与方解石连生。
3.2 毒砂
毒砂是样品中另一种主要的金属硫化物,含量为3.47%。该样品中毒砂的平均粒度为24.67 μm,呈细粒状态嵌布。具体粒度分布情况见表10。
表10 矿石中毒砂粒度分布统计结果
Table 10
| 粒级/μm | 毒砂 | |
|---|---|---|
| 相对含量/% | 正累积含量/% | |
| -74+53 | 8.48 | 8.48 |
| -53+43 | 9.47 | 17.95 |
| -43+38 | 2.31 | 20.26 |
| -38+20 | 27.84 | 48.09 |
| -20+15 | 14.89 | 62.98 |
| -15+10 | 16.85 | 79.83 |
| -10+5 | 10.51 | 90.34 |
| -5 | 9.66 | 100.00 |
研究表明,以单体形式存在的毒砂占45.43%,解离度在80%~100%之间的连生体占43.73%,其他解离程度的毒砂占10.84%,可知样品中的毒砂主要以单体和连生体形式存在,其中连生状态的毒砂主要与黄铁矿和白云石紧密连生。
4 影响金回收的矿物学因素分析
矿石中自然金和银金矿的平均粒经分别为3.06 μm和2.16 μm,均呈细粒—微细粒嵌布,提高磨矿细度,使部分包裹金裸露出来,有利于提高金的回收率。
根据检测分析结果可知,裸露金中的金含量约占金总量的72.71%,此部分金在浸出工艺中得到回收;对于以包裹形式存在的金,因不能直接与浸出药剂作用,必须通过细磨才可回收;另外,金矿物与含砷矿物连生关系密切,且该矿石中砷含量较高(1.44%),砷在回收金的过程中生成的沉淀可能会影响金的浸出效果。因此,在浸出之前,采取相应措施进行脱砷处理尤为重要。
5 结论
(1)该矿石含金5.36×10-6,金为唯一有价元素,金矿物主要为自然金和银金矿。矿物中金属矿物占30.77%,主要为黄铁矿、磁铁矿、毒砂和磁黄铁矿等;脉石矿物占69.23%,主要为方解石、石英、云母类和白云石类,含少量或微量的磷灰石、高岭石和滑石等。
(2)该矿石样品中金矿物粒度以细粒金和微细粒金为主,分别占49.43%和50.57%,最大颗粒金矿物为一自然金颗粒,粒度为16.40 μm×13.60 μm。通过提高磨矿细度,使部分包裹金裸露出来,有利于提高金的回收率。
(3)当该矿石粒度-200目占70%时,样品中金矿物的赋存状态以裸露金(连生金与单体金)为主,占72.71%,包裹金(晶间金与包裹金)占27.29%。
(4)矿石中的毒砂在浸出过程中易阻碍金的浸出,降低金的回收率,因此,在浸出之前,应采取相应措施预先氧化毒砂,消除毒砂在浸金过程中的不利影响,从而提高金的回收率。
参考文献
工艺矿物学在矿产资源找矿和综合利用中的应用
[J].
Application of technological mineralogy in prospecting and comprehensive utilization of mineral resources
[J].
工艺矿物学在选矿工艺研究中的作用及影响
[J].
The role and influence of technological mineralogy in the study of mineral processing technology
[J].
工艺矿物学近十年的主要进展
[J].
The main advances of process mineralogy in China in the last decade
[J].
某铜硫尾矿中钨的工艺矿物学研究
[J].
The process mineralogy of tungsten from a copper-sulfur tailings
[J].
金矿石的工艺矿物学研究
[J].
Research on process mineralogy of gold ore
[J].
低品位双重难处理金矿石工艺矿物学及浸金影响因素
[J].
Process mineralogy of low-grade double refractory gold ore and influencing factor on gold leaching
[J].
工艺矿物学研究的新技术与新理念
[J].
New techniques and concepts in process mineralogy
[J].
Automated scanning electron microscope based mineral liberation analysis
[J].
国外工艺矿物学进展及发展趋势
[J].
Process mineralogy progress and its trend abroad
[J].
MLA自动检测技术在工艺矿物学研究中的应用
[J].
Application of MLA automatic measurement technology in process mineralogy research
[J].
某氰渣工艺矿物学及金浮选工艺研究
[J].
Study on the gold flotation technology and process mineralogy of a cyanide residue
[J].
Rare earth element deportment studies utilising QEMSCAN technology
[J].
MLA系统在磷块岩工艺矿物学研究中的应用
[J].
MLA system's application in phosphate mineralogy study
[J].
澳大利亚昆士兰州某铝土矿工艺矿物学研究
[J].
Research on process mineralogy for a bauxite ore in Queensland,Australia
[J].
电子探针在本溪某深部铁矿石工艺矿物学研究中的应用
[J].
Application of EPMA in the processing mineralogy study of a deep iron ore in Benxi,Liaoning Province
[J].
山东某金矿中金的赋存状态研究
[J].
Research on gold occurrence state of some gold ore in shandong
[J].
某金矿工艺矿物学研究
[C]//
Technological mineralogy of a gold mine
[C]//Proceedings of the Academic Exchange of Prospecting Theory and Practice in Deep Mines, Research and Mineralogy of Mining Technology.
In-situ LA-ICP-MS trace elemental analyses of magnetite:Cu-(Au,Fe) deposits in the Khetri copper belt in Rajasthan Province,NW India
[J].
工艺矿物学参数自动测量技术研究
[J].
Research into the automatic measurement technology of process mineralogy parameters
[J].
工艺矿物学自动测试系统BPMA的研制及应用
[J].
Development and application of bgrimm process mineralogy analyzing system (BPMA)
[J].
基于Thermo Fisher能谱仪的工艺矿物学自动分析系统
[J].
Automatic analysis system of process mineralogy based on Thermo Fisher energy spectrometer
[J].



 甘公网安备 62010202000672号
甘公网安备 62010202000672号