随着浅部资源日渐枯竭,金属矿山的开采作业逐步向深部转移,掘进巷道热害问题越来越显著,严重影响了工作人员的身体健康和工作效率(张超等,2015;Zhang et al.,2019;聂兴信等,2020),制约采掘工程的正常施工。长距离掘进巷道中围岩对风流的加热作用增强而导致掘进作业面温度过高,无法满足作业需求。因此,研究深部长距离高温掘进巷道的降温技术对深井采矿具有重要意义。
多年来,国内外学者在理论预测与应用方面对长距离掘进巷道热害控制进行了大量研究。国外人工制冷降温技术发展较成熟(Filek et al.,2006;Wilson et al.,2011),热电联产降温及液氮注入等新技术逐步应用于采掘工作面的热害治理中(Chorowski et al.,2012;Shi et al.,2015)。国内对深井热害治理的研究相对较晚,在冷负荷预测和局部制冷降温方面的研究仍有不足。郭平业等(2011)建立反向分析冷负荷计算模型,亓玉栋(2014)提出动态冷负荷概念,为井下热害治理冷量计算提供理论基础。邹声华等(2016)采用隔热分流排热降温技术实现短距离掘进巷道的非人工制冷降温,田龙等(2020)在掘进巷道中利用辅助通风设施提高通风降温效果,但非人工制冷并不能有效治理深井长距离掘进巷道的热害问题。近年来,矿井空调降温逐步成为热害治理的主要手段(何满潮等,2008;刘娜等,2016),然而人工制冷热害治理中送风方式和送风参数的不同将会直接影响冷量利用。杜翠凤等(2016)通过降温实验得出增加一定风量可以降低巷道内温度,但送风量增加到一定值后降温效果不再显著;张瑞明等(2018)通过实验总结出掘进巷道温度在压入式通风6 min后迅速降低,12 min后巷道温度虽然降低但降温梯度大幅减小;李俊生(2014)通过对比不同通风方式下的掘进面降温效果,得出混合通风降温效果较差;辛松等(2020)研究得出混合通风中抽出风量高于压入风量时,对巷道内热害治理有利。以上研究表明,冷风的输送方式及参数设定是决定降温效果的主要因素,现有研究针对混合通风有效降温距离短的问题并未解决。
本文针对混合通风降温中压入风筒输送的冷空气未与环境充分热交换就被抽出风筒,迅速排出导致大量冷风浪费问题,提出改进型变距离双压入冷风抽压混合通风技术方案,通过改变送风方式来提高混合通风降温效果,利用Fluent数值模拟研究双压入风筒送风位置对混合通风有效降温距离的影响规律。
1 双压入式混合通风降温方案设计
河南某高温金矿巷道掘进采用抽压混合局部通风方式,抽压混合式通风结合压入式和抽出式通风的优点可将长巷道爆破后的粉尘快速排出,因此应用在该矿山掘进中。经实测,井下掘进巷道围岩温度高达38 ℃,掘进面附近环境温度高达34 ℃。为了能够有效地治理井下高温掘进巷道的热害问题,本文在现有传统抽压混合通风条件下,改变送风方式用一组压入风筒输送冷风,通过调整压入风筒2出风口位置治理不同区域热害问题。
1.1 双风筒送风降温原理
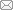
双压入抽压混合通风中,抽出式风筒与压入风筒1接近掘进工作面,压入风筒2布置位置取决于巷道内作业所需降温范围,如图1所示。2个压入式风筒分工不同,其中布置于近掘进面的风筒服务于掘进面的除尘降温工作,布置于中间位置的压入式风筒服务于掘进巷道温度调节,提高冷风利用效率。通过调整压入风筒2的布置位置降低长距离掘进巷道内环境温度,减少热害问题。添加压入风筒的目的不是增加送风量,而是分配压入风量,从而减少冷风浪费。将压入风筒2布置于掘进巷道作业需求地点,既能保证抽压混合通风的除尘工作,又可降低掘进作业范围的温度改善作业环境。
图1
图1
双压入混合通风三维模型
Fig.1
Three-dimensional model of double press-in mixed ventilation
1.2 降温通风计算及模型建立
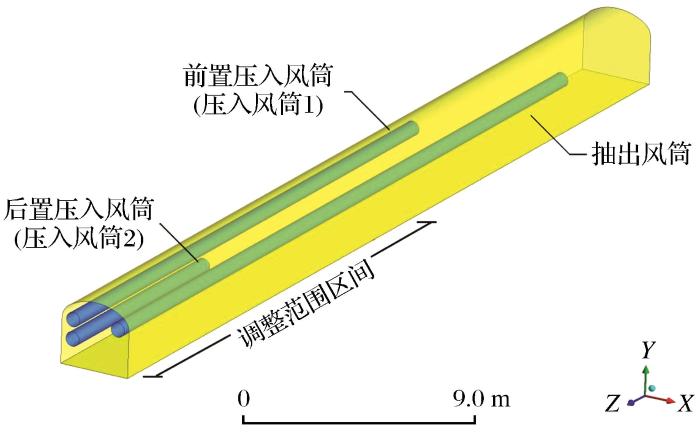
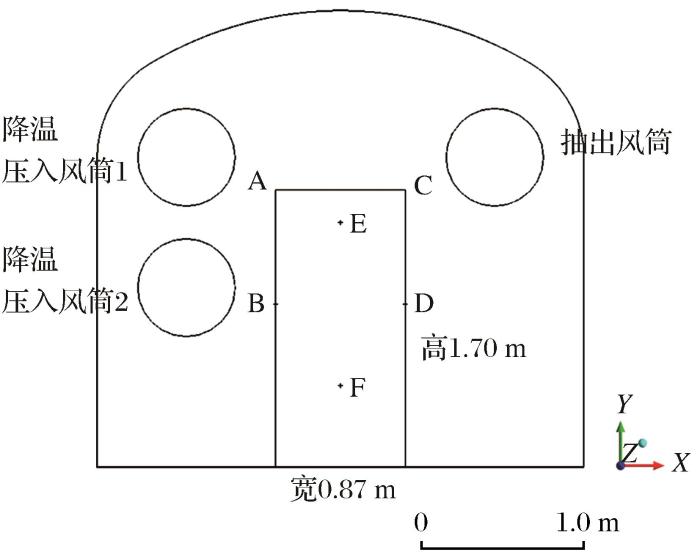
图2
图2
双压入混合通风风筒位置示意图
Fig.2
Schematic diagram of the position of the double press-in mixed ventilation duct
(1)风筒风量设计
爆破作业完成后立即通风除尘、降温,利用排尘风速(吴超,2008)计算风量:
式中:Q1为排出掘进工作面粉尘压入风量(m3/s);v0为巷道内排尘风速(m/s),经实测确定巷道内平均风速为0.442 m/s;A为巷道总断面面积,为7.83 m2。由
(2)风筒布置位置
抽压混合风筒布置时,压入风筒出口抽出风筒入口到掘进工作面的距离范围由经验公式(吴超,2008)确定,分别表示为
式中:L压为压入风筒出口距离掘进工作面的距离(m);L抽为抽出风筒入口距离掘进工作面的距离(m)。由此计算出抽压风筒分别距掘进工作面的距离范围,本文确定压入式风筒距掘进面14 m,抽出式风筒距掘进面4.5 m,由于爆破冲击波在0~4 m最大,在4~6 m内冲击波衰减较大,在6~8 m冲击波较为稳定(孔德森等,2012),所以确定抽出式风筒位置为距离掘进面6 m。
1.3 边界条件及网格划分
表1 条件设定
Table 1
| 边界条件 | 设置类型 |
|---|---|
| 压入风筒 | VELOCITY-INLET |
| 抽出风筒 | VELOCITY-INLET |
| 巷道入口 | PRESSURE-OUT |
| 送风温度/K | 295.15(22 ℃) |
| 巷道环境初始温度/K | 307.15(34 ℃) |
| 围岩壁面温度/K | 311.15(38 ℃) |
| 围岩厚度/m | 1.5 |
表2 求解器参数
Table 2
| 参数名称 | 设置类型 |
|---|---|
| 求解器 | 非稳态求解器 |
| 时间 | 20 min |
| 湍流模式 | k-ε模型 |
| 能量方程 | 开 |
| 压力速度耦合方式 | SIMPLEC |
| 收敛标准 | 0.001 |
几何模型的创建和网格划分在Gambit软件中完成,网格划分采用hex/wedge六面体网格,其中压入风筒2出风口布置于距掘进面30 m处时,模型网格数量约651 000;布置于50 m处时,模型网格数量约978 000;布置于70 m处时,模型网格数量约1 034 000,网格质量均良好。
2 降温对比方案设计
为研究双压入混合通风中压入风筒2布置位置对掘进巷道降温范围的影响,设置3组对比试验,其中控制变量为压入风筒2距掘进面的距离,其他送风参数不变,送风温度设为295.15 K (22 ℃)。具体方案见表3。
3 数值模拟结果分析
3.1 双压入混合通风温度场分析
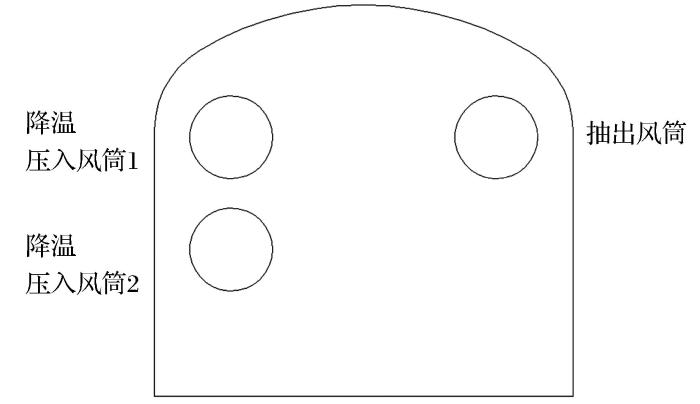
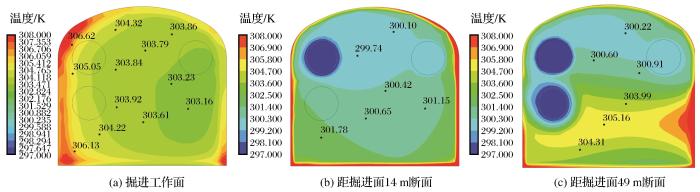
图3
图3
巷道内1.5 m水平高度的温度场分布云图
Fig.3
Temperature field distribution nephogram of 1.5 m horizontal height in roadway
图4
由于压入风筒2输送的冷风在贴附作用下沿围岩向前移动,此时抽出风筒对其吸卷作用不明显,故巷道内压入侧温度更低;而随着风流流动,抽出风筒的吸附作用加强导致冷风向抽出风筒侧汇聚,巷道内抽出测温度下降明显,所以巷道内温度先是压入侧温度较低之后转变为抽出测温度较低;由于压入风筒2输送的冷风在向前流动的过程中与环境充分热交换后温度升高,而压入风筒1输送的冷风作用范围较短,掘进面附近温度下降明显,所以巷道内温度出现小幅波动;在压入风筒2附近由于冷风与围岩及地面贴附作用使得近地面附近温度比中间高度的温度低,风流在抽出风筒的吸附作用下向上方聚集,故巷道内上方温度也较低。
3.2 压入风筒2布置位置对于巷道内温度分布的影响
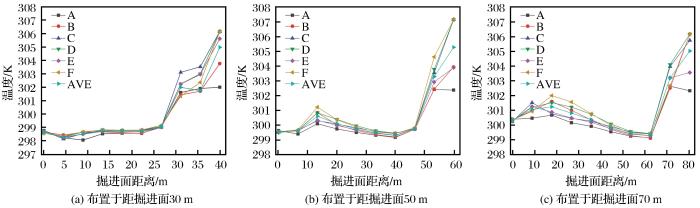
图5
将压入风筒2分别布置于距掘进面30,50,70 m位置按对比方案进行试验模拟,监测点温度变化曲线如图6所示。
图6
图6
不同风筒布位下的巷道监测点温度
Fig.6
Temperature of roadway monitoring points under different air duct layouts
由图6(a)可知,当压入风筒2布置于距掘进面30 m处时,掘进巷道30 m范围内温度分布均匀,可以保持在26 ℃左右,降温效果良好。巷道内没有出现温度波动且数值较低,说明压入风筒2的布置位置适宜,压入风筒1与压入风筒2输送的冷风共同作用使巷道30 m范围内作业环境较佳。
由图6 (b) 可知,压入风筒2布置于距掘进面50 m处时,巷道内温度整体比布置于30 m处时高约1 ℃,且在距掘进面14 m处出现明显的温度升高,巷道内出现温度波动说明压入风筒2布置位置将超出最有效降温距离,但即使巷道内温度出现波动,整体仍能保持在矿山规范要求值以下,故压入风筒2布置于距掘进面50 m处可以满足作业需求。
由图6 (c) 可知,压入风筒2布置于距掘进面70 m处时,巷道内温度明显较高,温度波动幅度更大,6个监测点位置的温度出现大范围超出限值,推断出巷道断面内其他范围的温度更不能满足作业需求,布置于距掘进面70 m处时双压入混合通风降温作用失效,说明70 m的选址超出了降温有效作用距离。
4 结论
(1)双压入式混合通风可有效作用于距掘进面50 m热交换最为活跃的重点治理区域,巷道内温度随远离掘进面距离的增加先升高再降低,出现约1 ℃小幅波动,整体温度保持在矿山限定28 ℃以内,综合降温效果良好。
(2)降温压入风筒2布分别置于30,50,70 m处时,随着压入风筒2布置位置的外移,巷道内降温范围增加但温度也随之升高,当压入风筒2布置于70 m处时,双压入混合通风降温作用基本失效。
(3)在制冷送风参数适当条件下灵活布置压入风筒2位置,可满足长距离巷道降温需求,当压入风筒2布置于距掘进面50 m以内时有较好的降温效果。本研究可为其他类似工程施工降温提供参考,同时也为其他高温掘进巷道通风降温技术方案设计中参数选取提供借鉴。
http://www.goldsci.ac.cn/article/2022/1005-2518/1005-2518-2022-30-1-85.shtml
参考文献
Air condition system for copper mine based on triseneration system
[J].
Numerical simulation of ventilation and cooling in excavation roadway and analysis of influencing factors
[J].
Calorific effect in evaporator from mine compression refrigerator with different refrigerants
[J].
Numerical simulation of dust distribution with far-pressing-near-absorption ventilation in an excavation roadway of high-altitude mine
[J].
Back-analysis algorithm of cooling load in deep mines
[J].
Research and development of HEMS coolings system and heat-harm control in deep mine
[J].
The dissemination rule of blasting shock-wave in subway tunnel
[J].
Research on Ventilation Mode of High Temperature Tunnel Face Temperature Drop Effect
[D].
Design and application of automatic cooling system in driving face
[J].
Influence of heat and humidity environment on function of human body in high temperature mine
[J].
Research on the Prediction of Dynamic Cooling Load and Control Technology in High Temperature Coal
[D].
Application of a novel liquid nitrogen control technique for heat stress and fire prevention in underground mines
[J].
Numerical simulation of temperature distribution in mining area of high temperature mine with auxiliary ventilation
[J].
Heat and moisture source distribution determination and analysis of long distance excavation roadway
[J].
Design and construction of a surface air cooling and refrigeration installation at a South African mine
[J].
Influence of different ventilation parameters on cooling of driving face
[J].
Experimental study of the heavy-duty working condition and intensified fatigue grade for the workmen under high temperature and great humidity environment
[J].
Experimental study on ventilation and cooling in excavation roadway
[J].
Research on heat transfer enhancement and flow characteristic of heat exchange surface in cosine style runner
[J].
Numerical simulation study on sectional cooling of long-distance excavation roadway in metal mine
[J].
On the air-partition for cooling with the heat- insulated plate
[J].
掘进巷道通风降温的数值模拟及影响因素分析
[J].
高海拔矿山掘进面长压短抽式通风粉尘分布数值模拟
[J].
深井降温冷负荷反分析计算方法
[J].
HEMS深井降温系统研发及热害控制对策
[J].
爆炸冲击波在地铁隧道内的传播规律研究
[J].
基于通风方式对高温隧道掌子面温降效果的研究
[D].
掘进工作面自动降温系统设计与应用
[J].
高温矿井热湿环境对人体机能的影响
[J].
高温矿井动态冷负荷预测与控制技术研究
[D].
配备辅助通风的高温矿井采掘区温度分布数值模拟
[J].
长距离掘进巷道热湿源分布的测定与分析
[J].
不同通风参数对掘进工作面降温的影响
[J].
高温高湿环境下人员劳动负荷与疲劳水平试验研究
[J].
掘进巷道通风降温试验研究
[J].
金属矿长距离掘进巷道分段降温数值模拟研究
[J].
掘进巷道隔热分流排热降温技术的理论与实践研究
[J].



 甘公网安备 62010202000672号
甘公网安备 62010202000672号