漂塘钨锡矿为石英脉型黑钨矿,矿脉倾向和走向具分支、复合现象,采用浅孔留矿法(小采)与阶段矿房法(大采)开采,采场顶板一般为石英脉与变质砂岩交替出现。矿区采空区带来的安全隐患问题备受关注,然而,因矿岩脉状交替出现,且矿脉倾向、走向变化极其复杂,基于模拟仿真等方式进行的采空区稳定性分析结果并不理想。基于未确知测度理论的采空区稳定性评价通过多因素的定性、定量评价,权重取值,为矿岩交替出现型矿床采空区稳定性分析提供了成功案例。本文针对漂塘矿区石英脉型钨矿山特点,基于未确知测度计算理论,提出了采幅和顶板暴露面积两大定量分级指标,构建了采空区危险性评价体系及分级标准,对矿区191个采空区进行了稳定性评价与分析,以期为实际生产提供指导。
1 未确知测度计算理论
1.1 单指标测度
设某评价对象有m 个影响因素,每个影响因素有p 个评价等级,用μjk =μ 表征实测值xj (j =1,2,…,m )属于第k 个评价等级Ck (k =1,2,…,p )的程度,则有单指标(影响因素)评价矩阵:
μ j k m p = μ 11 μ 12 … μ 1 p μ 21 μ 22 … μ 2 p ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ μ m 1 μ m 2 … μ m p (1)
当且仅当每个影响因素各个评价等级Ck 的程度与μ 之间满足归一性、可加性,即满足式(2)~式(4),则称μ 为未确知测度,简称测度,以上矩阵称为单指标测度评价矩阵。
0≤μ(xjk k (2)
μ(xjk (3)
μ x j k ∈ ∪ i = 1 k c k = ∑ i = 1 k μ x j k ∈ C k ( k = 1,2 , … , p ) (4)
1.2 指标权重的确定
完成单影响因素的评价后,进行各影响因素在整个评价体系中权重的确定,假定各影响因素j 的权重为wj ,则有
∑ j = 1 n w j = 1,1 > w j > 0 , ( j = 1,2 , … , m ) (5)
基于极大熵理论,以客观事实为主体,将主观内容作为约束条件,进行权重确定:
w j = e x p - 1 + δ ∑ k = 1 p ( 1 - r ) 2 j k / ( 1 - δ ) ∑ j = 1 m e x p - 1 + δ ∑ k = 1 p ( 1 - r ) 2 j k / ( 1 - δ ) ,
j = 1,2 , … , m (6)
式中:r j k = u j k / 1 m ∑ j = 1 m u j k δ <1,依评价指标重要程度个数进行取值,值越大,表示其个数越少,本研究取0.1。
1.3 多指标综合测度评价向量
令µk =µ 为单个评价对象的第k 个评价等级Ck 的程度,则有
μ k = ∑ j = 1 m w j μ j k ( k = 1,2 , … , p ) (7)
显然有0≤µk ≤1以及∑ k = 1 p μ k = 1 μ 1 , μ 2 , … , μ p
1.4 置信度识别准则
基于置信度识别准则,进行对象的最后评价,设λ 为置信度(λ ≥0.5),若C 1 >C 2 >… Cp ,且令
k 0 = m i n k : ∑ k = 1 k μ k ≥ λ , ( k = 1,2 , … , p ) (8)
2 采空区危险性评价体系及分级标准
针对漂塘矿区采空区失稳的原因,选择岩体结构(S1 )、地质构造(S2 )、地下可见水(S3 )、地下水体影响(S4 )、周围开采影响(S5 )、相邻空区情况(S6 )、工程布置(S7 )、采幅(S8 )、顶板暴露面积(S9 )、矿柱尺寸和布置(S10 )以及采空区的形状规格(S11 )共11项影响因子作为采空区稳定性影响因素,对采空区的稳定性进行评价。
采空区稳定性分级标准及岩体结构等9项定性影响因子取值标准参考了相关文献(宫凤强等,2008 ),整体上根据采空区分布情况、空区暴露面积和体积以及矿柱布设等情况,将采空区稳定程度划分为稳定(Ⅰ级)、一般稳定(Ⅱ级)、较不稳定(Ⅲ级)和不稳定(Ⅳ级)4个等级;各定性影响因子也划分为4个影响程度等级,并分别赋值1、2、3和4。根据采空区稳定性分级标准及石英脉开采实践,对采幅和顶板暴露面积2个定量指标进行分级取值,如表1 所示。
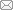
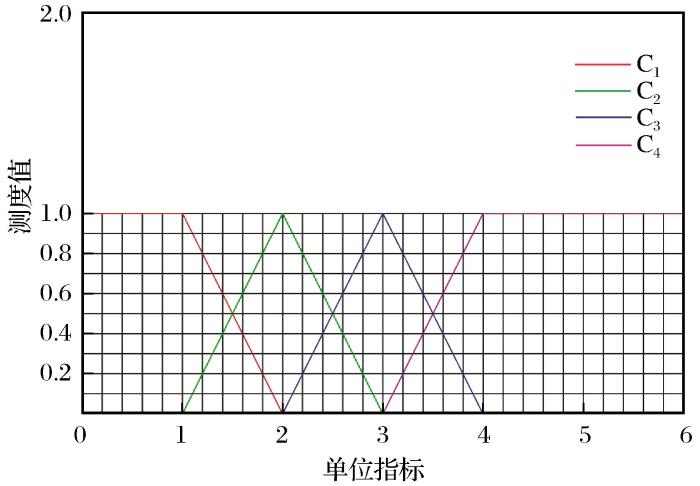
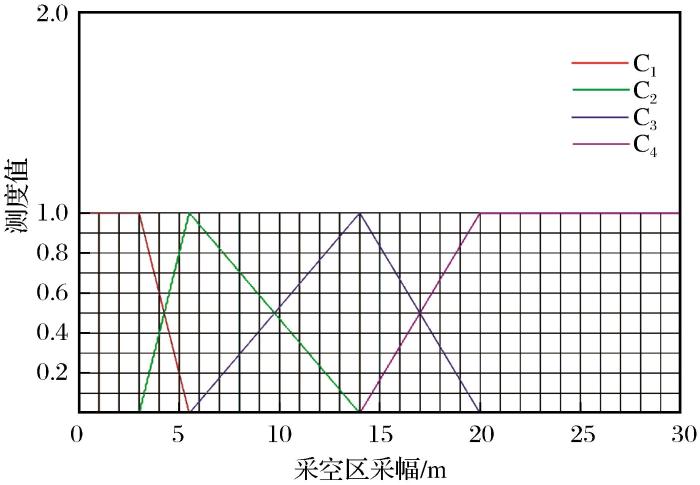
根据定量和定性指标分级标准构建单指标未确知测度函数,如图1 ~图3 所示。
图1
图1
采空区定性指标单指标未确知测度函数
Fig.1
Single index uncertainty measurement function of qualitative indicators of goaf
图2
图2
采空区采幅单指标未确知测度函数
Fig.2
Single index uncertainty measurement function of goaf span
图3
图3
采空区顶板暴露面积单指标未确知测度函数
Fig.3
Single index uncertainty measurement function of goaf roof exposure area
3 工程实例应用
3.1 采空区稳定性评价
漂塘矿区经多年开采,遗留了大量未处理采空区。这些空区除少量进行了废石充填处理之外,其他均施以封闭处理,空区顶板暴露,仅由矿柱自支撑。随着开采向深部延伸,采空区体积不断增大,采空区稳定性每况愈下,地压显现越发明显,上部采空区已成为深部开采最大的安全隐患。为此,对于268~616 m中段空区调查获取的191个采空区进行稳定性评价,为后续采空区处理及残矿回收提供指导依据。
表2 所示为部分空区评价指标取值,现以388中段Ⅲ126采空区为例进行采空区稳定性评价。根据单指标测度函数(图1 ~图3 )可求得Ⅲ126采场单指标未确知测度评价矩阵为
( μ j k ) 11 × 4 = 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0.829 0.171 0 0 0 0 0 1 0.444 0.556 0 0 (9)
由式(5)和式(6)确定该空区各指标权重向量为:w 式(7)求得多指标综合测度评价向量为(0.1717,0.2390,0.0406,0.5487),基于置信度识别准则,即式(8)可得k 0 =4,故388中段Ⅲ126采空区的稳定性等级为Ⅳ级。
遵循以上评价步骤,完成各空区稳定性评价,部分空区多指标综合测度评价向量及其稳定性评价结果见表3 。
3.2 评价结果分析
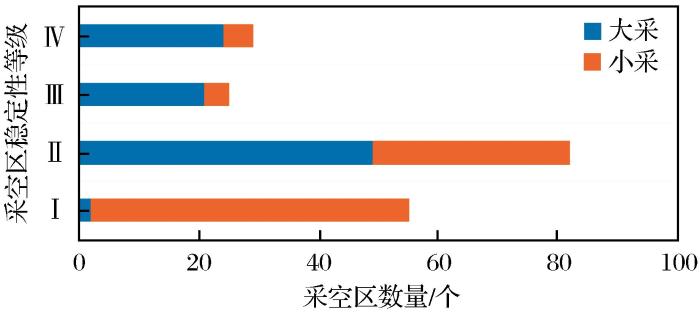
(1)小采空区的稳定性普遍高于大采空区。稳定性分级结果显示,本次调查的191个采空区中,稳定(Ⅰ)的有55个,一般稳定(Ⅱ)的有82个,较不稳定(Ⅲ)的有25个,不稳定(Ⅳ)的有29个。稳定性分级在大采或小采中的分布情况如图4 所示,其中,小采稳定性等级以稳定和一般稳定为主,占比分别为55.8%和34.7%;大采稳定性评价等级普遍更高,稳定与不稳定基本各占一半,一般稳定占51.0%、较不稳定占21.9%、不稳定占25.0%。
图4
图4
采空区稳定性评价结果分布情况
Fig.4
Distribution of evaluation results of goaf stability
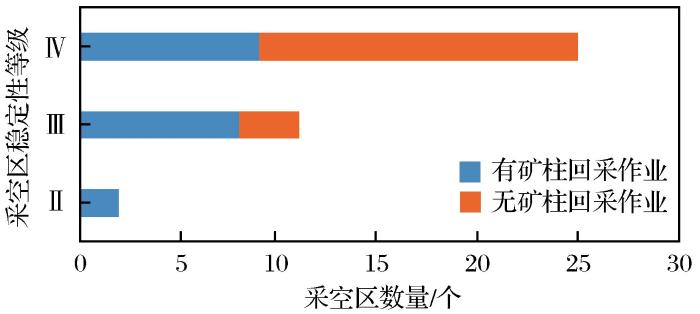
(2)矿柱的回收作业极大地加速了采空区的破坏。调查发现,现有采空区中已破坏的采空区有38个,无矿柱回采作业或曾有矿柱回采作业的采空区各占一半,38个已破坏的采空区稳定性评价结果如图5 所示。无矿柱回采作业的已破坏采空区稳定性评价结果以不稳定为主,占比为84.2%,这也侧面证明了分析的准确性与可靠性;有矿柱回采作业的已破坏采空区稳定性评价结果中不稳定占比相对更低,占比为47.4%,其余52.6%为一般稳定和较不稳定的采空区,这是由于矿柱回采作业加速了采空区的失稳破坏。
图5
图5
已破坏采空区稳定性评价结果分布情况
Fig.5
Distribution of stability evaluation results of damaged goaf
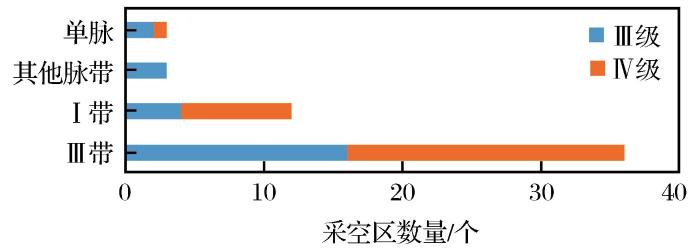
(3)评价结果为Ⅲ级或Ⅳ级的空区主要分布在脉带中(图6 )。评价结果中较不稳定采空区为25个,主要分布在脉带中,其中Ⅲ带占比为64.0%,Ⅰ带占比为16.0%;评价结果中不稳定采空区有29个,Ⅲ带占比为69.0%,Ⅰ带占比为27.6%。
图6
图6
较不稳定与不稳定采空区矿脉分布情况
Fig.6
Distribution of ore veins in relatively unstable and unstable goaf
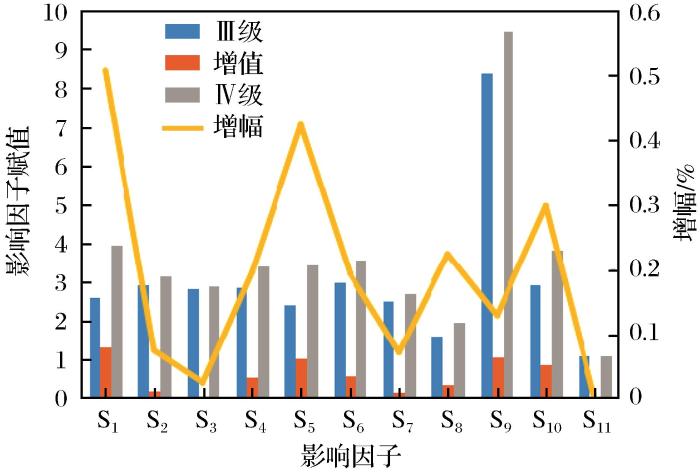
(4)就漂塘矿区而言,采场采幅不宜超过16 m,暴露面积不宜超过800 m2 。取漂塘矿区191个采空区中采空区稳定性评价结果为Ⅲ级与Ⅳ级的54个采空区,对比分析二者影响因子的平均取值,如图7 所示。由图7 可知,除采空区的规格形状(S11 )之外,Ⅳ级的其他影响因子较Ⅲ级的均有所增加,增幅大小不一,以岩体结构(S1 )、周围开采影响(S5 )以及矿柱尺寸和布置(S10 )增幅最大,三者是造成采空区稳定性下降的最大变量因素,采幅与顶板暴露面积的增加是漂塘矿区采空区稳定性下降的主要影响因子。矿区岩体以石英脉和变质砂岩为主,岩体结构以完整岩块为主,但对于脉带矿体,当采幅增宽、顶板暴露面积增大、矿柱尺寸和布置变化不大时,矿岩接触带极大地弱化了矿柱的稳定性,极易受周围开采、相邻空区情况及地下水体影响,空区出现顶板冒落、矿柱崩塌,直至采空区失稳破坏。
图7
图7
采空区稳定性影响因子分析
Fig.7
Impact factor analysis of goaf stability
综合现有调查数据,Ⅲ级采空区平均采幅为16 m,顶板暴露面积为841 m2 ;Ⅳ级采空区平均采幅为19.6 m,顶板暴露面积为950 m2 。因此,建议当采场采幅超过16 m或暴露面积超过800 m2 时,要适当增大矿柱尺寸,并注意周围开采活动、地质构造、相邻空区及地下水对采空区的影响,以确保采空区的稳定。采空区处理及矿柱回收工作也要统筹考虑、统一实施,确保空区处理安全,并最大限度地回收残矿资源。
4 结论
(1)就漂塘矿区而言,浅孔留矿法单脉开采空区稳定性普遍高于阶段矿房法脉带开采空区,评价结果为较不稳定或不稳定的采空区以脉带为主,矿柱的回收极大地加速了空区的失稳破坏,而空场采幅及空场暴露面积是控制该类矿体采空区稳定性的主要因素,对于该矿区而言,采幅为16 m、空场暴露面积为800 m2 是其保持稳定性的一个限值。
(2)鉴于评价结果与矿区空区稳定性实际情况高度契合,认为基于未确知测度理论的空区稳定性评价为石英脉型钨矿山采空区稳定性评价提供了新的途径,且本文中的采幅与顶板暴露面积两大定量分级标准可在同类型矿山采空区稳定性评价中推广使用。
http://www.goldsci.ac.cn/article/2021/1005-2518/1005-2518-2021-29-3-433.shtml
参考文献
View Option
[]
Cheng Aibao Wang Xinmin Liu Hongqiang 2011 .Application of gray hierarchy analysis in the stability evaluation of underground mined-out areas
[J].Metal Mine ,40 (2 ):17 -21 .
Cheng Li Liu Huanxin Zhu Mingde al et 2020 .Current situation and prospect of research on underground goaf in metal mines
[J].Gold Science and Technology ,28 (1 ):70 -81 .
Deng Gao Yang Shan 2017 .Stability evaluation of goafs based on combined forecasting and variable precision rough fuzzy set
[J].Gold Science and Technology ,25 (3 ):98 -107 .
Du Kun Li Xibing Liu Kewei al et 2011 .Comprehensive evaluation of underground goaf risk and engineering application
[J].Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology) ,42 (9 ):2802 -2811 .
Fu Wubin Deng Kazhong Zhang Liya 2011 .Stability analysis of coal pillar in goaf by room-column method
[J].Safety in Coal Mines ,42 (1 ):136 -139 .
Gong Fengqiang Li Xibing Dong Longjun al et 2008 .Underground goaf risk evaluation based on uncertainty measure theory
[J].Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering ,27 (2 ):323 -330 .
Hao Xubin Yang Lihui Wan Sheng 2013 .Stability evaluation for mine gob areas based on AHP and fuzzy synthetic judgement theory
[J].Gold Science and Technology ,21 (6 ):63 -67 .
Huang Yinghua Xu Bigen Tang Shaohui 2009 .Study on the damage pattern sand mechanism of mined-out area in mines using room-and-pillar mining method
[J].Mining Research & Development ,29 (4 ):24 -26 .
Kou Xiangyu Jia Mingtao Wang Liguan al et 2010 .Evaluation and analysis of stability of mined-out area based on the CMS and DIMINE-FLAC3D coupling technique
[J].Mineral Engineering Research ,25 (1 ):31 -35 .
Liu Muyu Xu Changyou 2000 .Stability analysis of pillars in mined-out area
[J].Mining and Metallurgical Engineering ,20 (1 ):19 -22 .
Luo Zhouquan Liu Xiaoming Wu Yabin al et 2008 .Study on cavity stability numerical simulation based on coupling of Surpac and Phase2
[J].Journal of Liaoning Technical University(Natural Science) ,27 (4 ):485 -488 .
Song Weidong Fu Jianxin Du Jianhua al et 2012 .Analysis of stability of goaf group in metal mines based on precision detection
[J].Rock and Soil Mechanics ,33 (12 ):3781 -3787 .
Tang Shuo Luo Zhouquan Xu Hai 2012 .Evaluation of stability of goaf based on fuzzy matter-element theory
[J].China Safety Science Journal ,22 (7 ):24 -30 .
Wang Jilin Jiang Bo 2005 .Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of stability in a coal mine area
[J].Ground Pressure and Strata Control ,(2 ):29 -31 ,34 .
Wang Xinmin Ding Deqiang Duan Yu 2006 .Applications of the grey relation analysis in the evaluation of the risk degree of the underground mined-out stopes
[J].Journal of Safety Science and Technology ,(4 ):35 -39 .
Wu Qihong Wan Shiming Peng Wenxiang 2012 .A comprehensive evaluation method about stability of polylaminate goafs
[J].Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology) ,43 (6 ):2324 -2330 .
Xie Xingzhi 2014 .Study on stability of roof-coal pillar in room and pillar mining goaf in shallow depth seam
[J].Coal Science and Technology ,42 (7 ):1 -4 ,9 .
Yang Yang Feng Naiqi Yu Zhenyou al et 2008 .Comprehensive stability evaluation for mined-out areas based on AHP and fuzzy mathematics
[J].Nonferrous Metals (Mining Section) ,(5 ):37 -39 ,42 .
Zhang Jian Zhang Yuanfang Yuan Tiezhu al et 2010 .Analysis and appraisal for stabiliy of goaf
[J].Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering ,8 (2 ):145 -146 ,155 .
Zhang Lin Sun Guoquan Li Tongpeng al et 2013 .Research of detection and comprehensive treatment of underground mine goaf and its application
[J].Metal Mine ,42 (11 ):1 -4 ,138 .
程爱宝 ,王新民 ,刘洪强 2011 .灰色层次分析法在地下采空区稳定性评价中的应用
[J].金属矿山 ,40 (2 ):17 -21 .
[本文引用: 1]
程力 ,刘焕新 ,朱明德 ,等 2020 .金属矿山地下采空区问题研究现状与展望
[J].黄金科学技术 ,28 (1 ):70 -81 .
[本文引用: 1]
邓高 ,杨珊 2017 .基于组合预测与变精度粗糙模糊集的采空区稳定性评价
[J].黄金科学技术 ,25 (3 ):98 -107 .
[本文引用: 1]
杜坤 ,李夕兵 ,刘科伟 ,等 2011 .采空区危险性评价的综合方法及工程应用
[J].中南大学学报(自然科学版) ,42 (9 ):2802 -2811 .
[本文引用: 1]
付武斌 ,邓喀中 ,张立亚 2011 .房柱式采空区煤柱稳定性分析
[J].煤矿安全 ,42 (1 ):136 -139 .
[本文引用: 1]
宫凤强 ,李夕兵 ,董陇军 ,等 2008 .基于未确知测度理论的采空区危险性评价研究
[J].岩石力学与工程学报 ,27 (2 ):323 -330 .
[本文引用: 2]
郝旭彬 ,杨立辉 ,万胜 2013 .基于AHP及模糊综合评判法的采空区稳定性评价
[J].黄金科学技术 ,21 (6 ):63 -67 .
[本文引用: 1]
黄英华 ,徐必根 ,唐绍辉 2009 .房柱法开采矿山采空区失稳模式及机理
[J].矿业研究与开发 ,29 (4 ):24 -26 .
[本文引用: 1]
寇向宇 ,贾明涛 ,王李管 ,等 2010 .基于CMS及DIMINE-FLAC3D 耦合技术的采空区稳定性分析与评价
[J].矿业工程研究 ,25 (1 ):31 -35 .
[本文引用: 1]
刘沐宇 ,徐长佑 2000 .地下采空区矿柱稳定性分析
[J].矿冶工程 ,20 (1 ):19 -22 .
[本文引用: 1]
罗周全 ,刘晓明 ,吴亚斌 ,等 2008 .基于Surpac和Phase2 耦合的采空区稳定性模拟分析
[J].辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版) ,27 (4 ):485 -488 .
[本文引用: 1]
宋卫东 ,付建新 ,杜建华 ,等 2012 .基于精密探测的金属矿山采空区群稳定性分析
[J].岩土力学 ,33 (12 ):3781 -3787 .
[本文引用: 1]
唐硕 ,罗周全 ,徐海 2012 .基于模糊物元的采空区稳定性评价研究
[J].中国安全科学学报 ,22 (7 ):24 -30 .
[本文引用: 1]
汪吉林 ,姜波 2005 .煤矿采空区稳定性的模糊综合评判
[J].矿山压力与顶板管理 ,(2 ):29 -31 ,34 .
[本文引用: 1]
王新民 ,丁德强 ,段瑜 2006 .灰色关联分析在地下采空区危险度评价中的应用
[J].中国安全生产科学技术 ,(4 ):35 -39 .
[本文引用: 1]
吴启红 ,万世明 ,彭文祥 2012 .一种多层采空区群稳定性的综合评价法
[J].中南大学学报(自然科学版) ,43 (6 ):2324 -2330 .
[本文引用: 1]
解兴智 2014 .浅埋煤层房柱式采空区顶板—煤柱稳定性研究
[J].煤炭科学技术 ,42 (7 ):1 -4 ,9 .
[本文引用: 1]
杨扬 ,冯乃琦 ,余珍友 ,等 2008 .基于层次分析和模糊数学的采空区稳定性综合评价
[J].有色金属(矿山部分) ,(5 ):37 -39 ,42 .
[本文引用: 1]
张建 ,张远芳 ,袁铁柱 ,等 2010 .采空区稳定性分析与评价
[J].水利与建筑工程学报 ,8 (2 ):145 -146 ,155 .
[本文引用: 1]
章林 ,孙国权 ,李同鹏 ,等 2013 .地下矿山采空区探测及综合治理研究与应用
[J].金属矿山 ,42 (11 ):1 -4 ,138 .
[本文引用: 1]
Application of gray hierarchy analysis in the stability evaluation of underground mined-out areas
0
2011
Current situation and prospect of research on underground goaf in metal mines
0
2020
Stability evaluation of goafs based on combined forecasting and variable precision rough fuzzy set
0
2017
Comprehensive evaluation of underground goaf risk and engineering application
0
2011
Stability analysis of coal pillar in goaf by room-column method
0
2011
Underground goaf risk evaluation based on uncertainty measure theory
0
2008
Stability evaluation for mine gob areas based on AHP and fuzzy synthetic judgement theory
0
2013
Study on the damage pattern sand mechanism of mined-out area in mines using room-and-pillar mining method
0
2009
Evaluation and analysis of stability of mined-out area based on the CMS and DIMINE-FLAC3D coupling technique
0
2010
Stability analysis of pillars in mined-out area
0
2000
Study on cavity stability numerical simulation based on coupling of Surpac and Phase2
0
2008
Analysis of stability of goaf group in metal mines based on precision detection
0
2012
Evaluation of stability of goaf based on fuzzy matter-element theory
0
2012
Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of stability in a coal mine area
0
2005
Applications of the grey relation analysis in the evaluation of the risk degree of the underground mined-out stopes
0
2006
A comprehensive evaluation method about stability of polylaminate goafs
0
2012
Study on stability of roof-coal pillar in room and pillar mining goaf in shallow depth seam
0
2014
Comprehensive stability evaluation for mined-out areas based on AHP and fuzzy mathematics
0
2008
Analysis and appraisal for stabiliy of goaf
0
2010
Research of detection and comprehensive treatment of underground mine goaf and its application
0
2013
灰色层次分析法在地下采空区稳定性评价中的应用
1
2011
... 受空场法开采影响,采空区所诱发的塌陷和沉降已成为各类金属矿山的主要灾害之一,极大地危害着人员与设备的安全(程力等,2020 ).随着行业科技工作者对空区危害认识的提升,采空区稳定性评估越来越受到重视.现阶段采空区稳定性分析主要通过模拟仿真方式进行,模拟平台主要有FLAC3D 、Ansys、3DEC和Phase2 等,基于采空区扫描、三维建模及三维数值计算的耦合方法也为采空区稳定性分析提供了新途径(罗周全等,2008 ;章林等,2013 ;宋卫东等,2012 ;寇向宇等,2010 ).采空区稳定性评价是基于采空区稳定性影响因子评价,并依据一种或多种理论进行权重或关联计算,最终实现采空区稳定性评价,常用的理论有物元理论(杜坤等,2011 ;唐硕等,2012 )、层次分析法(程爱宝等,2011 ;郝旭彬等,2013 ;杨扬等,2008 )、灰色关联法(王新民等,2006 )、未确知测度理论模糊评判(宫凤强等,2008 )和模糊评判(吴启红等,2012 ;邓高等,2017 ;汪吉林等,2005 )等.关于结构稳定性分析,解兴智(2014) 、付武斌等(2011) 和黄英华等(2009) 对房柱法开采后空区顶板、矿柱进行了失稳研究;张建等(2010) 以力学平衡为依据,基于不同的力学原理,进行上覆岩层临界厚度计算,最终通过抗滑安全系数实现采空区的分析评价;刘沐宇等(2000) 则通过点安全系数法和可靠度分析法进行了矿柱稳定性分析. ...
金属矿山地下采空区问题研究现状与展望
1
2020
... 受空场法开采影响,采空区所诱发的塌陷和沉降已成为各类金属矿山的主要灾害之一,极大地危害着人员与设备的安全(程力等,2020 ).随着行业科技工作者对空区危害认识的提升,采空区稳定性评估越来越受到重视.现阶段采空区稳定性分析主要通过模拟仿真方式进行,模拟平台主要有FLAC3D 、Ansys、3DEC和Phase2 等,基于采空区扫描、三维建模及三维数值计算的耦合方法也为采空区稳定性分析提供了新途径(罗周全等,2008 ;章林等,2013 ;宋卫东等,2012 ;寇向宇等,2010 ).采空区稳定性评价是基于采空区稳定性影响因子评价,并依据一种或多种理论进行权重或关联计算,最终实现采空区稳定性评价,常用的理论有物元理论(杜坤等,2011 ;唐硕等,2012 )、层次分析法(程爱宝等,2011 ;郝旭彬等,2013 ;杨扬等,2008 )、灰色关联法(王新民等,2006 )、未确知测度理论模糊评判(宫凤强等,2008 )和模糊评判(吴启红等,2012 ;邓高等,2017 ;汪吉林等,2005 )等.关于结构稳定性分析,解兴智(2014) 、付武斌等(2011) 和黄英华等(2009) 对房柱法开采后空区顶板、矿柱进行了失稳研究;张建等(2010) 以力学平衡为依据,基于不同的力学原理,进行上覆岩层临界厚度计算,最终通过抗滑安全系数实现采空区的分析评价;刘沐宇等(2000) 则通过点安全系数法和可靠度分析法进行了矿柱稳定性分析. ...
基于组合预测与变精度粗糙模糊集的采空区稳定性评价
1
2017
... 受空场法开采影响,采空区所诱发的塌陷和沉降已成为各类金属矿山的主要灾害之一,极大地危害着人员与设备的安全(程力等,2020 ).随着行业科技工作者对空区危害认识的提升,采空区稳定性评估越来越受到重视.现阶段采空区稳定性分析主要通过模拟仿真方式进行,模拟平台主要有FLAC3D 、Ansys、3DEC和Phase2 等,基于采空区扫描、三维建模及三维数值计算的耦合方法也为采空区稳定性分析提供了新途径(罗周全等,2008 ;章林等,2013 ;宋卫东等,2012 ;寇向宇等,2010 ).采空区稳定性评价是基于采空区稳定性影响因子评价,并依据一种或多种理论进行权重或关联计算,最终实现采空区稳定性评价,常用的理论有物元理论(杜坤等,2011 ;唐硕等,2012 )、层次分析法(程爱宝等,2011 ;郝旭彬等,2013 ;杨扬等,2008 )、灰色关联法(王新民等,2006 )、未确知测度理论模糊评判(宫凤强等,2008 )和模糊评判(吴启红等,2012 ;邓高等,2017 ;汪吉林等,2005 )等.关于结构稳定性分析,解兴智(2014) 、付武斌等(2011) 和黄英华等(2009) 对房柱法开采后空区顶板、矿柱进行了失稳研究;张建等(2010) 以力学平衡为依据,基于不同的力学原理,进行上覆岩层临界厚度计算,最终通过抗滑安全系数实现采空区的分析评价;刘沐宇等(2000) 则通过点安全系数法和可靠度分析法进行了矿柱稳定性分析. ...
采空区危险性评价的综合方法及工程应用
1
2011
... 受空场法开采影响,采空区所诱发的塌陷和沉降已成为各类金属矿山的主要灾害之一,极大地危害着人员与设备的安全(程力等,2020 ).随着行业科技工作者对空区危害认识的提升,采空区稳定性评估越来越受到重视.现阶段采空区稳定性分析主要通过模拟仿真方式进行,模拟平台主要有FLAC3D 、Ansys、3DEC和Phase2 等,基于采空区扫描、三维建模及三维数值计算的耦合方法也为采空区稳定性分析提供了新途径(罗周全等,2008 ;章林等,2013 ;宋卫东等,2012 ;寇向宇等,2010 ).采空区稳定性评价是基于采空区稳定性影响因子评价,并依据一种或多种理论进行权重或关联计算,最终实现采空区稳定性评价,常用的理论有物元理论(杜坤等,2011 ;唐硕等,2012 )、层次分析法(程爱宝等,2011 ;郝旭彬等,2013 ;杨扬等,2008 )、灰色关联法(王新民等,2006 )、未确知测度理论模糊评判(宫凤强等,2008 )和模糊评判(吴启红等,2012 ;邓高等,2017 ;汪吉林等,2005 )等.关于结构稳定性分析,解兴智(2014) 、付武斌等(2011) 和黄英华等(2009) 对房柱法开采后空区顶板、矿柱进行了失稳研究;张建等(2010) 以力学平衡为依据,基于不同的力学原理,进行上覆岩层临界厚度计算,最终通过抗滑安全系数实现采空区的分析评价;刘沐宇等(2000) 则通过点安全系数法和可靠度分析法进行了矿柱稳定性分析. ...
房柱式采空区煤柱稳定性分析
1
2011
... 受空场法开采影响,采空区所诱发的塌陷和沉降已成为各类金属矿山的主要灾害之一,极大地危害着人员与设备的安全(程力等,2020 ).随着行业科技工作者对空区危害认识的提升,采空区稳定性评估越来越受到重视.现阶段采空区稳定性分析主要通过模拟仿真方式进行,模拟平台主要有FLAC3D 、Ansys、3DEC和Phase2 等,基于采空区扫描、三维建模及三维数值计算的耦合方法也为采空区稳定性分析提供了新途径(罗周全等,2008 ;章林等,2013 ;宋卫东等,2012 ;寇向宇等,2010 ).采空区稳定性评价是基于采空区稳定性影响因子评价,并依据一种或多种理论进行权重或关联计算,最终实现采空区稳定性评价,常用的理论有物元理论(杜坤等,2011 ;唐硕等,2012 )、层次分析法(程爱宝等,2011 ;郝旭彬等,2013 ;杨扬等,2008 )、灰色关联法(王新民等,2006 )、未确知测度理论模糊评判(宫凤强等,2008 )和模糊评判(吴启红等,2012 ;邓高等,2017 ;汪吉林等,2005 )等.关于结构稳定性分析,解兴智(2014) 、付武斌等(2011) 和黄英华等(2009) 对房柱法开采后空区顶板、矿柱进行了失稳研究;张建等(2010) 以力学平衡为依据,基于不同的力学原理,进行上覆岩层临界厚度计算,最终通过抗滑安全系数实现采空区的分析评价;刘沐宇等(2000) 则通过点安全系数法和可靠度分析法进行了矿柱稳定性分析. ...
基于未确知测度理论的采空区危险性评价研究
2
2008
... 受空场法开采影响,采空区所诱发的塌陷和沉降已成为各类金属矿山的主要灾害之一,极大地危害着人员与设备的安全(程力等,2020 ).随着行业科技工作者对空区危害认识的提升,采空区稳定性评估越来越受到重视.现阶段采空区稳定性分析主要通过模拟仿真方式进行,模拟平台主要有FLAC3D 、Ansys、3DEC和Phase2 等,基于采空区扫描、三维建模及三维数值计算的耦合方法也为采空区稳定性分析提供了新途径(罗周全等,2008 ;章林等,2013 ;宋卫东等,2012 ;寇向宇等,2010 ).采空区稳定性评价是基于采空区稳定性影响因子评价,并依据一种或多种理论进行权重或关联计算,最终实现采空区稳定性评价,常用的理论有物元理论(杜坤等,2011 ;唐硕等,2012 )、层次分析法(程爱宝等,2011 ;郝旭彬等,2013 ;杨扬等,2008 )、灰色关联法(王新民等,2006 )、未确知测度理论模糊评判(宫凤强等,2008 )和模糊评判(吴启红等,2012 ;邓高等,2017 ;汪吉林等,2005 )等.关于结构稳定性分析,解兴智(2014) 、付武斌等(2011) 和黄英华等(2009) 对房柱法开采后空区顶板、矿柱进行了失稳研究;张建等(2010) 以力学平衡为依据,基于不同的力学原理,进行上覆岩层临界厚度计算,最终通过抗滑安全系数实现采空区的分析评价;刘沐宇等(2000) 则通过点安全系数法和可靠度分析法进行了矿柱稳定性分析. ...
... 采空区稳定性分级标准及岩体结构等9项定性影响因子取值标准参考了相关文献(宫凤强等,2008 ),整体上根据采空区分布情况、空区暴露面积和体积以及矿柱布设等情况,将采空区稳定程度划分为稳定(Ⅰ级)、一般稳定(Ⅱ级)、较不稳定(Ⅲ级)和不稳定(Ⅳ级)4个等级;各定性影响因子也划分为4个影响程度等级,并分别赋值1、2、3和4.根据采空区稳定性分级标准及石英脉开采实践,对采幅和顶板暴露面积2个定量指标进行分级取值,如表1 所示. ...
基于AHP及模糊综合评判法的采空区稳定性评价
1
2013
... 受空场法开采影响,采空区所诱发的塌陷和沉降已成为各类金属矿山的主要灾害之一,极大地危害着人员与设备的安全(程力等,2020 ).随着行业科技工作者对空区危害认识的提升,采空区稳定性评估越来越受到重视.现阶段采空区稳定性分析主要通过模拟仿真方式进行,模拟平台主要有FLAC3D 、Ansys、3DEC和Phase2 等,基于采空区扫描、三维建模及三维数值计算的耦合方法也为采空区稳定性分析提供了新途径(罗周全等,2008 ;章林等,2013 ;宋卫东等,2012 ;寇向宇等,2010 ).采空区稳定性评价是基于采空区稳定性影响因子评价,并依据一种或多种理论进行权重或关联计算,最终实现采空区稳定性评价,常用的理论有物元理论(杜坤等,2011 ;唐硕等,2012 )、层次分析法(程爱宝等,2011 ;郝旭彬等,2013 ;杨扬等,2008 )、灰色关联法(王新民等,2006 )、未确知测度理论模糊评判(宫凤强等,2008 )和模糊评判(吴启红等,2012 ;邓高等,2017 ;汪吉林等,2005 )等.关于结构稳定性分析,解兴智(2014) 、付武斌等(2011) 和黄英华等(2009) 对房柱法开采后空区顶板、矿柱进行了失稳研究;张建等(2010) 以力学平衡为依据,基于不同的力学原理,进行上覆岩层临界厚度计算,最终通过抗滑安全系数实现采空区的分析评价;刘沐宇等(2000) 则通过点安全系数法和可靠度分析法进行了矿柱稳定性分析. ...
房柱法开采矿山采空区失稳模式及机理
1
2009
... 受空场法开采影响,采空区所诱发的塌陷和沉降已成为各类金属矿山的主要灾害之一,极大地危害着人员与设备的安全(程力等,2020 ).随着行业科技工作者对空区危害认识的提升,采空区稳定性评估越来越受到重视.现阶段采空区稳定性分析主要通过模拟仿真方式进行,模拟平台主要有FLAC3D 、Ansys、3DEC和Phase2 等,基于采空区扫描、三维建模及三维数值计算的耦合方法也为采空区稳定性分析提供了新途径(罗周全等,2008 ;章林等,2013 ;宋卫东等,2012 ;寇向宇等,2010 ).采空区稳定性评价是基于采空区稳定性影响因子评价,并依据一种或多种理论进行权重或关联计算,最终实现采空区稳定性评价,常用的理论有物元理论(杜坤等,2011 ;唐硕等,2012 )、层次分析法(程爱宝等,2011 ;郝旭彬等,2013 ;杨扬等,2008 )、灰色关联法(王新民等,2006 )、未确知测度理论模糊评判(宫凤强等,2008 )和模糊评判(吴启红等,2012 ;邓高等,2017 ;汪吉林等,2005 )等.关于结构稳定性分析,解兴智(2014) 、付武斌等(2011) 和黄英华等(2009) 对房柱法开采后空区顶板、矿柱进行了失稳研究;张建等(2010) 以力学平衡为依据,基于不同的力学原理,进行上覆岩层临界厚度计算,最终通过抗滑安全系数实现采空区的分析评价;刘沐宇等(2000) 则通过点安全系数法和可靠度分析法进行了矿柱稳定性分析. ...
基于CMS及DIMINE-FLAC3D 耦合技术的采空区稳定性分析与评价
1
2010
... 受空场法开采影响,采空区所诱发的塌陷和沉降已成为各类金属矿山的主要灾害之一,极大地危害着人员与设备的安全(程力等,2020 ).随着行业科技工作者对空区危害认识的提升,采空区稳定性评估越来越受到重视.现阶段采空区稳定性分析主要通过模拟仿真方式进行,模拟平台主要有FLAC3D 、Ansys、3DEC和Phase2 等,基于采空区扫描、三维建模及三维数值计算的耦合方法也为采空区稳定性分析提供了新途径(罗周全等,2008 ;章林等,2013 ;宋卫东等,2012 ;寇向宇等,2010 ).采空区稳定性评价是基于采空区稳定性影响因子评价,并依据一种或多种理论进行权重或关联计算,最终实现采空区稳定性评价,常用的理论有物元理论(杜坤等,2011 ;唐硕等,2012 )、层次分析法(程爱宝等,2011 ;郝旭彬等,2013 ;杨扬等,2008 )、灰色关联法(王新民等,2006 )、未确知测度理论模糊评判(宫凤强等,2008 )和模糊评判(吴启红等,2012 ;邓高等,2017 ;汪吉林等,2005 )等.关于结构稳定性分析,解兴智(2014) 、付武斌等(2011) 和黄英华等(2009) 对房柱法开采后空区顶板、矿柱进行了失稳研究;张建等(2010) 以力学平衡为依据,基于不同的力学原理,进行上覆岩层临界厚度计算,最终通过抗滑安全系数实现采空区的分析评价;刘沐宇等(2000) 则通过点安全系数法和可靠度分析法进行了矿柱稳定性分析. ...
地下采空区矿柱稳定性分析
1
2000
... 受空场法开采影响,采空区所诱发的塌陷和沉降已成为各类金属矿山的主要灾害之一,极大地危害着人员与设备的安全(程力等,2020 ).随着行业科技工作者对空区危害认识的提升,采空区稳定性评估越来越受到重视.现阶段采空区稳定性分析主要通过模拟仿真方式进行,模拟平台主要有FLAC3D 、Ansys、3DEC和Phase2 等,基于采空区扫描、三维建模及三维数值计算的耦合方法也为采空区稳定性分析提供了新途径(罗周全等,2008 ;章林等,2013 ;宋卫东等,2012 ;寇向宇等,2010 ).采空区稳定性评价是基于采空区稳定性影响因子评价,并依据一种或多种理论进行权重或关联计算,最终实现采空区稳定性评价,常用的理论有物元理论(杜坤等,2011 ;唐硕等,2012 )、层次分析法(程爱宝等,2011 ;郝旭彬等,2013 ;杨扬等,2008 )、灰色关联法(王新民等,2006 )、未确知测度理论模糊评判(宫凤强等,2008 )和模糊评判(吴启红等,2012 ;邓高等,2017 ;汪吉林等,2005 )等.关于结构稳定性分析,解兴智(2014) 、付武斌等(2011) 和黄英华等(2009) 对房柱法开采后空区顶板、矿柱进行了失稳研究;张建等(2010) 以力学平衡为依据,基于不同的力学原理,进行上覆岩层临界厚度计算,最终通过抗滑安全系数实现采空区的分析评价;刘沐宇等(2000) 则通过点安全系数法和可靠度分析法进行了矿柱稳定性分析. ...
基于Surpac和Phase2 耦合的采空区稳定性模拟分析
1
2008
... 受空场法开采影响,采空区所诱发的塌陷和沉降已成为各类金属矿山的主要灾害之一,极大地危害着人员与设备的安全(程力等,2020 ).随着行业科技工作者对空区危害认识的提升,采空区稳定性评估越来越受到重视.现阶段采空区稳定性分析主要通过模拟仿真方式进行,模拟平台主要有FLAC3D 、Ansys、3DEC和Phase2 等,基于采空区扫描、三维建模及三维数值计算的耦合方法也为采空区稳定性分析提供了新途径(罗周全等,2008 ;章林等,2013 ;宋卫东等,2012 ;寇向宇等,2010 ).采空区稳定性评价是基于采空区稳定性影响因子评价,并依据一种或多种理论进行权重或关联计算,最终实现采空区稳定性评价,常用的理论有物元理论(杜坤等,2011 ;唐硕等,2012 )、层次分析法(程爱宝等,2011 ;郝旭彬等,2013 ;杨扬等,2008 )、灰色关联法(王新民等,2006 )、未确知测度理论模糊评判(宫凤强等,2008 )和模糊评判(吴启红等,2012 ;邓高等,2017 ;汪吉林等,2005 )等.关于结构稳定性分析,解兴智(2014) 、付武斌等(2011) 和黄英华等(2009) 对房柱法开采后空区顶板、矿柱进行了失稳研究;张建等(2010) 以力学平衡为依据,基于不同的力学原理,进行上覆岩层临界厚度计算,最终通过抗滑安全系数实现采空区的分析评价;刘沐宇等(2000) 则通过点安全系数法和可靠度分析法进行了矿柱稳定性分析. ...
基于精密探测的金属矿山采空区群稳定性分析
1
2012
... 受空场法开采影响,采空区所诱发的塌陷和沉降已成为各类金属矿山的主要灾害之一,极大地危害着人员与设备的安全(程力等,2020 ).随着行业科技工作者对空区危害认识的提升,采空区稳定性评估越来越受到重视.现阶段采空区稳定性分析主要通过模拟仿真方式进行,模拟平台主要有FLAC3D 、Ansys、3DEC和Phase2 等,基于采空区扫描、三维建模及三维数值计算的耦合方法也为采空区稳定性分析提供了新途径(罗周全等,2008 ;章林等,2013 ;宋卫东等,2012 ;寇向宇等,2010 ).采空区稳定性评价是基于采空区稳定性影响因子评价,并依据一种或多种理论进行权重或关联计算,最终实现采空区稳定性评价,常用的理论有物元理论(杜坤等,2011 ;唐硕等,2012 )、层次分析法(程爱宝等,2011 ;郝旭彬等,2013 ;杨扬等,2008 )、灰色关联法(王新民等,2006 )、未确知测度理论模糊评判(宫凤强等,2008 )和模糊评判(吴启红等,2012 ;邓高等,2017 ;汪吉林等,2005 )等.关于结构稳定性分析,解兴智(2014) 、付武斌等(2011) 和黄英华等(2009) 对房柱法开采后空区顶板、矿柱进行了失稳研究;张建等(2010) 以力学平衡为依据,基于不同的力学原理,进行上覆岩层临界厚度计算,最终通过抗滑安全系数实现采空区的分析评价;刘沐宇等(2000) 则通过点安全系数法和可靠度分析法进行了矿柱稳定性分析. ...
基于模糊物元的采空区稳定性评价研究
1
2012
... 受空场法开采影响,采空区所诱发的塌陷和沉降已成为各类金属矿山的主要灾害之一,极大地危害着人员与设备的安全(程力等,2020 ).随着行业科技工作者对空区危害认识的提升,采空区稳定性评估越来越受到重视.现阶段采空区稳定性分析主要通过模拟仿真方式进行,模拟平台主要有FLAC3D 、Ansys、3DEC和Phase2 等,基于采空区扫描、三维建模及三维数值计算的耦合方法也为采空区稳定性分析提供了新途径(罗周全等,2008 ;章林等,2013 ;宋卫东等,2012 ;寇向宇等,2010 ).采空区稳定性评价是基于采空区稳定性影响因子评价,并依据一种或多种理论进行权重或关联计算,最终实现采空区稳定性评价,常用的理论有物元理论(杜坤等,2011 ;唐硕等,2012 )、层次分析法(程爱宝等,2011 ;郝旭彬等,2013 ;杨扬等,2008 )、灰色关联法(王新民等,2006 )、未确知测度理论模糊评判(宫凤强等,2008 )和模糊评判(吴启红等,2012 ;邓高等,2017 ;汪吉林等,2005 )等.关于结构稳定性分析,解兴智(2014) 、付武斌等(2011) 和黄英华等(2009) 对房柱法开采后空区顶板、矿柱进行了失稳研究;张建等(2010) 以力学平衡为依据,基于不同的力学原理,进行上覆岩层临界厚度计算,最终通过抗滑安全系数实现采空区的分析评价;刘沐宇等(2000) 则通过点安全系数法和可靠度分析法进行了矿柱稳定性分析. ...
煤矿采空区稳定性的模糊综合评判
1
2005
... 受空场法开采影响,采空区所诱发的塌陷和沉降已成为各类金属矿山的主要灾害之一,极大地危害着人员与设备的安全(程力等,2020 ).随着行业科技工作者对空区危害认识的提升,采空区稳定性评估越来越受到重视.现阶段采空区稳定性分析主要通过模拟仿真方式进行,模拟平台主要有FLAC3D 、Ansys、3DEC和Phase2 等,基于采空区扫描、三维建模及三维数值计算的耦合方法也为采空区稳定性分析提供了新途径(罗周全等,2008 ;章林等,2013 ;宋卫东等,2012 ;寇向宇等,2010 ).采空区稳定性评价是基于采空区稳定性影响因子评价,并依据一种或多种理论进行权重或关联计算,最终实现采空区稳定性评价,常用的理论有物元理论(杜坤等,2011 ;唐硕等,2012 )、层次分析法(程爱宝等,2011 ;郝旭彬等,2013 ;杨扬等,2008 )、灰色关联法(王新民等,2006 )、未确知测度理论模糊评判(宫凤强等,2008 )和模糊评判(吴启红等,2012 ;邓高等,2017 ;汪吉林等,2005 )等.关于结构稳定性分析,解兴智(2014) 、付武斌等(2011) 和黄英华等(2009) 对房柱法开采后空区顶板、矿柱进行了失稳研究;张建等(2010) 以力学平衡为依据,基于不同的力学原理,进行上覆岩层临界厚度计算,最终通过抗滑安全系数实现采空区的分析评价;刘沐宇等(2000) 则通过点安全系数法和可靠度分析法进行了矿柱稳定性分析. ...
灰色关联分析在地下采空区危险度评价中的应用
1
2006
... 受空场法开采影响,采空区所诱发的塌陷和沉降已成为各类金属矿山的主要灾害之一,极大地危害着人员与设备的安全(程力等,2020 ).随着行业科技工作者对空区危害认识的提升,采空区稳定性评估越来越受到重视.现阶段采空区稳定性分析主要通过模拟仿真方式进行,模拟平台主要有FLAC3D 、Ansys、3DEC和Phase2 等,基于采空区扫描、三维建模及三维数值计算的耦合方法也为采空区稳定性分析提供了新途径(罗周全等,2008 ;章林等,2013 ;宋卫东等,2012 ;寇向宇等,2010 ).采空区稳定性评价是基于采空区稳定性影响因子评价,并依据一种或多种理论进行权重或关联计算,最终实现采空区稳定性评价,常用的理论有物元理论(杜坤等,2011 ;唐硕等,2012 )、层次分析法(程爱宝等,2011 ;郝旭彬等,2013 ;杨扬等,2008 )、灰色关联法(王新民等,2006 )、未确知测度理论模糊评判(宫凤强等,2008 )和模糊评判(吴启红等,2012 ;邓高等,2017 ;汪吉林等,2005 )等.关于结构稳定性分析,解兴智(2014) 、付武斌等(2011) 和黄英华等(2009) 对房柱法开采后空区顶板、矿柱进行了失稳研究;张建等(2010) 以力学平衡为依据,基于不同的力学原理,进行上覆岩层临界厚度计算,最终通过抗滑安全系数实现采空区的分析评价;刘沐宇等(2000) 则通过点安全系数法和可靠度分析法进行了矿柱稳定性分析. ...
一种多层采空区群稳定性的综合评价法
1
2012
... 受空场法开采影响,采空区所诱发的塌陷和沉降已成为各类金属矿山的主要灾害之一,极大地危害着人员与设备的安全(程力等,2020 ).随着行业科技工作者对空区危害认识的提升,采空区稳定性评估越来越受到重视.现阶段采空区稳定性分析主要通过模拟仿真方式进行,模拟平台主要有FLAC3D 、Ansys、3DEC和Phase2 等,基于采空区扫描、三维建模及三维数值计算的耦合方法也为采空区稳定性分析提供了新途径(罗周全等,2008 ;章林等,2013 ;宋卫东等,2012 ;寇向宇等,2010 ).采空区稳定性评价是基于采空区稳定性影响因子评价,并依据一种或多种理论进行权重或关联计算,最终实现采空区稳定性评价,常用的理论有物元理论(杜坤等,2011 ;唐硕等,2012 )、层次分析法(程爱宝等,2011 ;郝旭彬等,2013 ;杨扬等,2008 )、灰色关联法(王新民等,2006 )、未确知测度理论模糊评判(宫凤强等,2008 )和模糊评判(吴启红等,2012 ;邓高等,2017 ;汪吉林等,2005 )等.关于结构稳定性分析,解兴智(2014) 、付武斌等(2011) 和黄英华等(2009) 对房柱法开采后空区顶板、矿柱进行了失稳研究;张建等(2010) 以力学平衡为依据,基于不同的力学原理,进行上覆岩层临界厚度计算,最终通过抗滑安全系数实现采空区的分析评价;刘沐宇等(2000) 则通过点安全系数法和可靠度分析法进行了矿柱稳定性分析. ...
浅埋煤层房柱式采空区顶板—煤柱稳定性研究
1
2014
... 受空场法开采影响,采空区所诱发的塌陷和沉降已成为各类金属矿山的主要灾害之一,极大地危害着人员与设备的安全(程力等,2020 ).随着行业科技工作者对空区危害认识的提升,采空区稳定性评估越来越受到重视.现阶段采空区稳定性分析主要通过模拟仿真方式进行,模拟平台主要有FLAC3D 、Ansys、3DEC和Phase2 等,基于采空区扫描、三维建模及三维数值计算的耦合方法也为采空区稳定性分析提供了新途径(罗周全等,2008 ;章林等,2013 ;宋卫东等,2012 ;寇向宇等,2010 ).采空区稳定性评价是基于采空区稳定性影响因子评价,并依据一种或多种理论进行权重或关联计算,最终实现采空区稳定性评价,常用的理论有物元理论(杜坤等,2011 ;唐硕等,2012 )、层次分析法(程爱宝等,2011 ;郝旭彬等,2013 ;杨扬等,2008 )、灰色关联法(王新民等,2006 )、未确知测度理论模糊评判(宫凤强等,2008 )和模糊评判(吴启红等,2012 ;邓高等,2017 ;汪吉林等,2005 )等.关于结构稳定性分析,解兴智(2014) 、付武斌等(2011) 和黄英华等(2009) 对房柱法开采后空区顶板、矿柱进行了失稳研究;张建等(2010) 以力学平衡为依据,基于不同的力学原理,进行上覆岩层临界厚度计算,最终通过抗滑安全系数实现采空区的分析评价;刘沐宇等(2000) 则通过点安全系数法和可靠度分析法进行了矿柱稳定性分析. ...
基于层次分析和模糊数学的采空区稳定性综合评价
1
2008
... 受空场法开采影响,采空区所诱发的塌陷和沉降已成为各类金属矿山的主要灾害之一,极大地危害着人员与设备的安全(程力等,2020 ).随着行业科技工作者对空区危害认识的提升,采空区稳定性评估越来越受到重视.现阶段采空区稳定性分析主要通过模拟仿真方式进行,模拟平台主要有FLAC3D 、Ansys、3DEC和Phase2 等,基于采空区扫描、三维建模及三维数值计算的耦合方法也为采空区稳定性分析提供了新途径(罗周全等,2008 ;章林等,2013 ;宋卫东等,2012 ;寇向宇等,2010 ).采空区稳定性评价是基于采空区稳定性影响因子评价,并依据一种或多种理论进行权重或关联计算,最终实现采空区稳定性评价,常用的理论有物元理论(杜坤等,2011 ;唐硕等,2012 )、层次分析法(程爱宝等,2011 ;郝旭彬等,2013 ;杨扬等,2008 )、灰色关联法(王新民等,2006 )、未确知测度理论模糊评判(宫凤强等,2008 )和模糊评判(吴启红等,2012 ;邓高等,2017 ;汪吉林等,2005 )等.关于结构稳定性分析,解兴智(2014) 、付武斌等(2011) 和黄英华等(2009) 对房柱法开采后空区顶板、矿柱进行了失稳研究;张建等(2010) 以力学平衡为依据,基于不同的力学原理,进行上覆岩层临界厚度计算,最终通过抗滑安全系数实现采空区的分析评价;刘沐宇等(2000) 则通过点安全系数法和可靠度分析法进行了矿柱稳定性分析. ...
采空区稳定性分析与评价
1
2010
... 受空场法开采影响,采空区所诱发的塌陷和沉降已成为各类金属矿山的主要灾害之一,极大地危害着人员与设备的安全(程力等,2020 ).随着行业科技工作者对空区危害认识的提升,采空区稳定性评估越来越受到重视.现阶段采空区稳定性分析主要通过模拟仿真方式进行,模拟平台主要有FLAC3D 、Ansys、3DEC和Phase2 等,基于采空区扫描、三维建模及三维数值计算的耦合方法也为采空区稳定性分析提供了新途径(罗周全等,2008 ;章林等,2013 ;宋卫东等,2012 ;寇向宇等,2010 ).采空区稳定性评价是基于采空区稳定性影响因子评价,并依据一种或多种理论进行权重或关联计算,最终实现采空区稳定性评价,常用的理论有物元理论(杜坤等,2011 ;唐硕等,2012 )、层次分析法(程爱宝等,2011 ;郝旭彬等,2013 ;杨扬等,2008 )、灰色关联法(王新民等,2006 )、未确知测度理论模糊评判(宫凤强等,2008 )和模糊评判(吴启红等,2012 ;邓高等,2017 ;汪吉林等,2005 )等.关于结构稳定性分析,解兴智(2014) 、付武斌等(2011) 和黄英华等(2009) 对房柱法开采后空区顶板、矿柱进行了失稳研究;张建等(2010) 以力学平衡为依据,基于不同的力学原理,进行上覆岩层临界厚度计算,最终通过抗滑安全系数实现采空区的分析评价;刘沐宇等(2000) 则通过点安全系数法和可靠度分析法进行了矿柱稳定性分析. ...
地下矿山采空区探测及综合治理研究与应用
1
2013
... 受空场法开采影响,采空区所诱发的塌陷和沉降已成为各类金属矿山的主要灾害之一,极大地危害着人员与设备的安全(程力等,2020 ).随着行业科技工作者对空区危害认识的提升,采空区稳定性评估越来越受到重视.现阶段采空区稳定性分析主要通过模拟仿真方式进行,模拟平台主要有FLAC3D 、Ansys、3DEC和Phase2 等,基于采空区扫描、三维建模及三维数值计算的耦合方法也为采空区稳定性分析提供了新途径(罗周全等,2008 ;章林等,2013 ;宋卫东等,2012 ;寇向宇等,2010 ).采空区稳定性评价是基于采空区稳定性影响因子评价,并依据一种或多种理论进行权重或关联计算,最终实现采空区稳定性评价,常用的理论有物元理论(杜坤等,2011 ;唐硕等,2012 )、层次分析法(程爱宝等,2011 ;郝旭彬等,2013 ;杨扬等,2008 )、灰色关联法(王新民等,2006 )、未确知测度理论模糊评判(宫凤强等,2008 )和模糊评判(吴启红等,2012 ;邓高等,2017 ;汪吉林等,2005 )等.关于结构稳定性分析,解兴智(2014) 、付武斌等(2011) 和黄英华等(2009) 对房柱法开采后空区顶板、矿柱进行了失稳研究;张建等(2010) 以力学平衡为依据,基于不同的力学原理,进行上覆岩层临界厚度计算,最终通过抗滑安全系数实现采空区的分析评价;刘沐宇等(2000) 则通过点安全系数法和可靠度分析法进行了矿柱稳定性分析. ...



 甘公网安备 62010202000672号
甘公网安备 62010202000672号