 PDF(2293 KB)
PDF(2293 KB)


 PDF(2293 KB)
PDF(2293 KB)
 PDF(2293 KB)
PDF(2293 KB)
甘肃某复杂难处理金矿细菌氧化—氰化实验研究
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Experimental Study on Bacterial Oxidation-Cyanidation of a Complex Re-fractory Gold Mine in Gansu Province
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}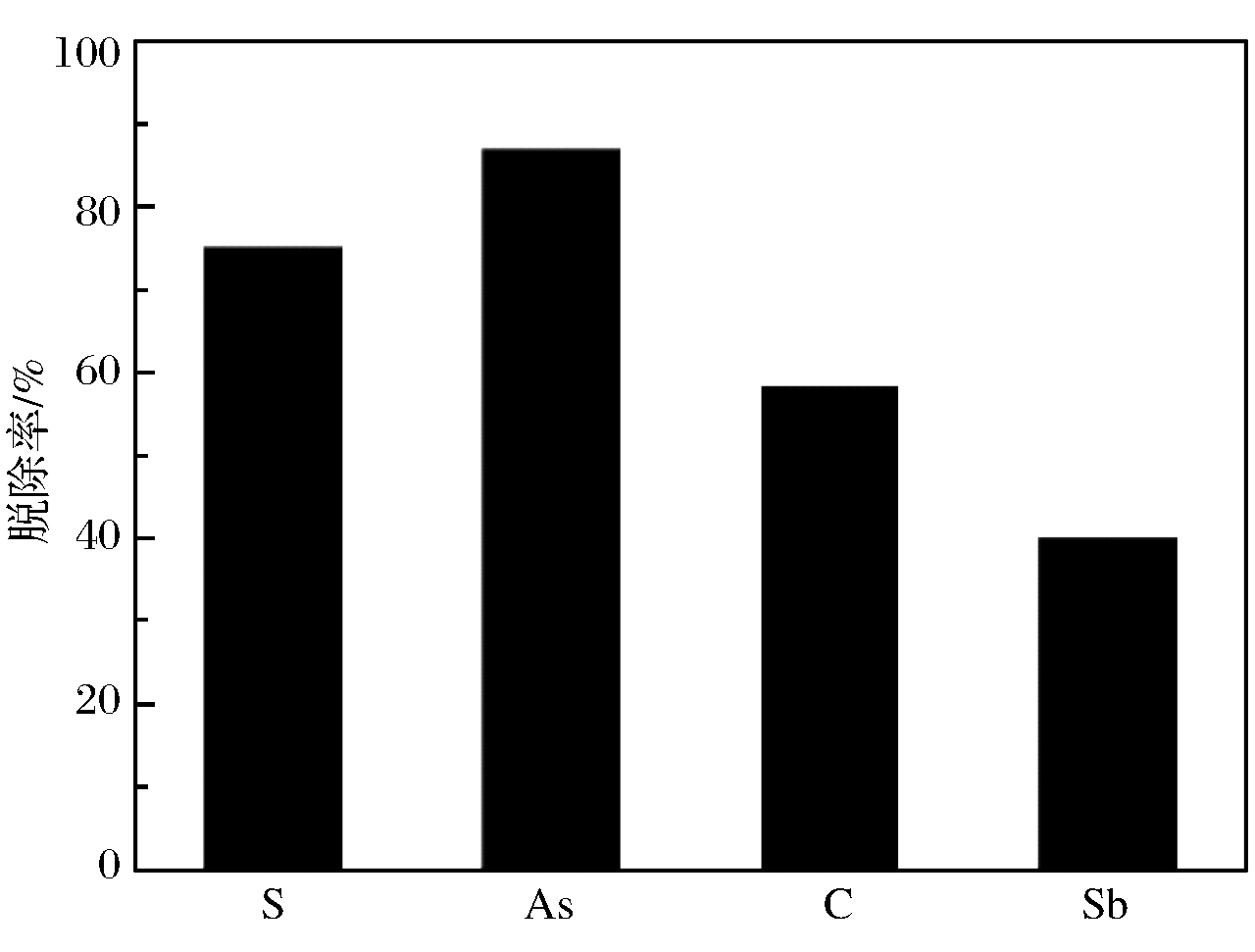
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |