 PDF(9475 KB)
PDF(9475 KB)


 PDF(9475 KB)
PDF(9475 KB)
 PDF(9475 KB)
PDF(9475 KB)
赣南印支期白石钨(铜)矿床成矿岩体地球化学特征及地质意义
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Geochemical Characteristics and Geological Significance of the Ore-forming Granite of Indosinian Baishi W-Cu Deposit in Southern Jiangxi Province
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}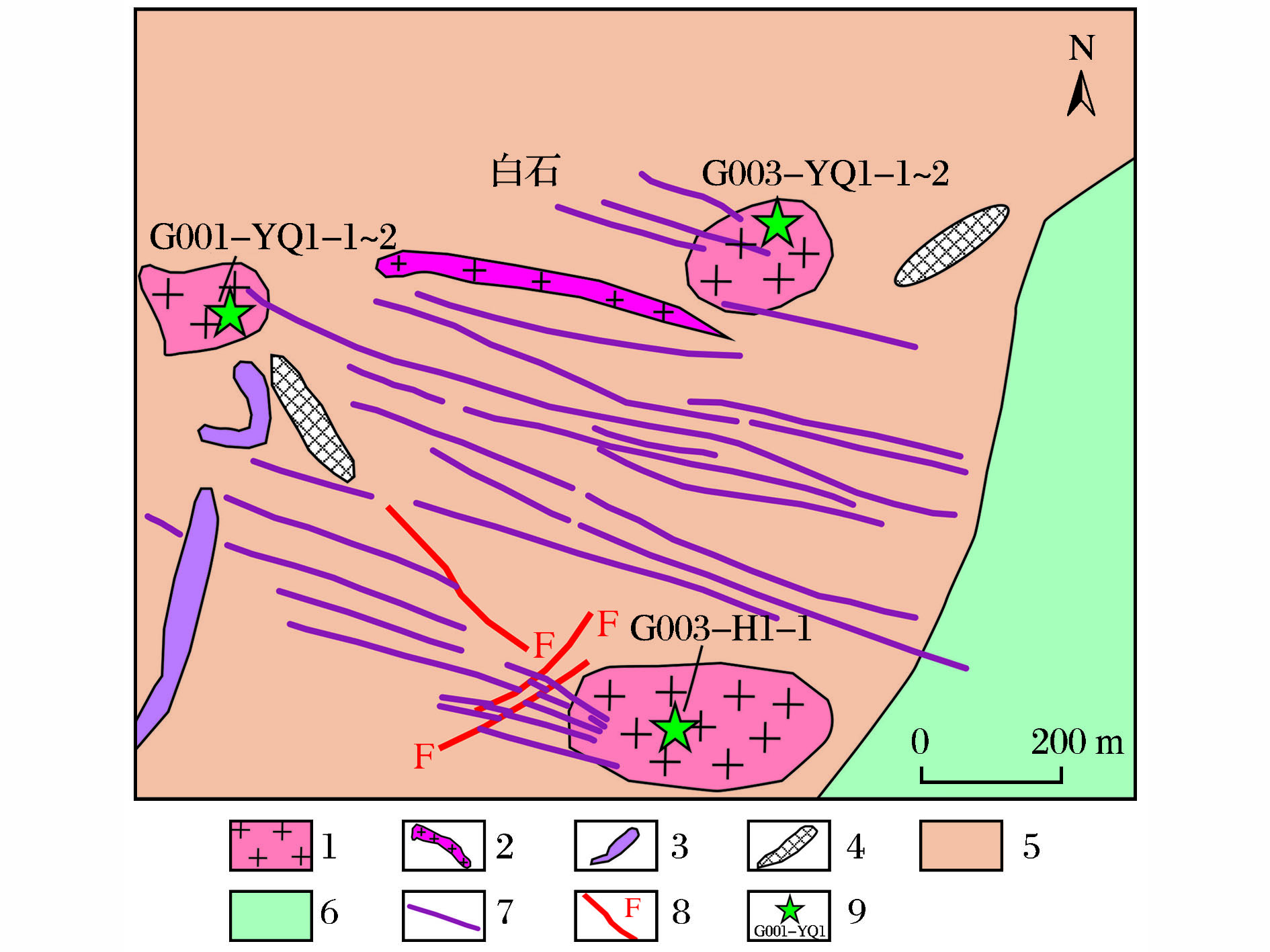
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |