 PDF(4576 KB)
PDF(4576 KB)


 PDF(4576 KB)
PDF(4576 KB)
 PDF(4576 KB)
PDF(4576 KB)
基于启发式遗传算法的地下采场作业计划优化模型
 ({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_cn}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}Optimization Model of Underground Stope Working Plan Based on Heuristic Genetic Algorithm
 ({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
({{custom_author.role_en}}), {{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}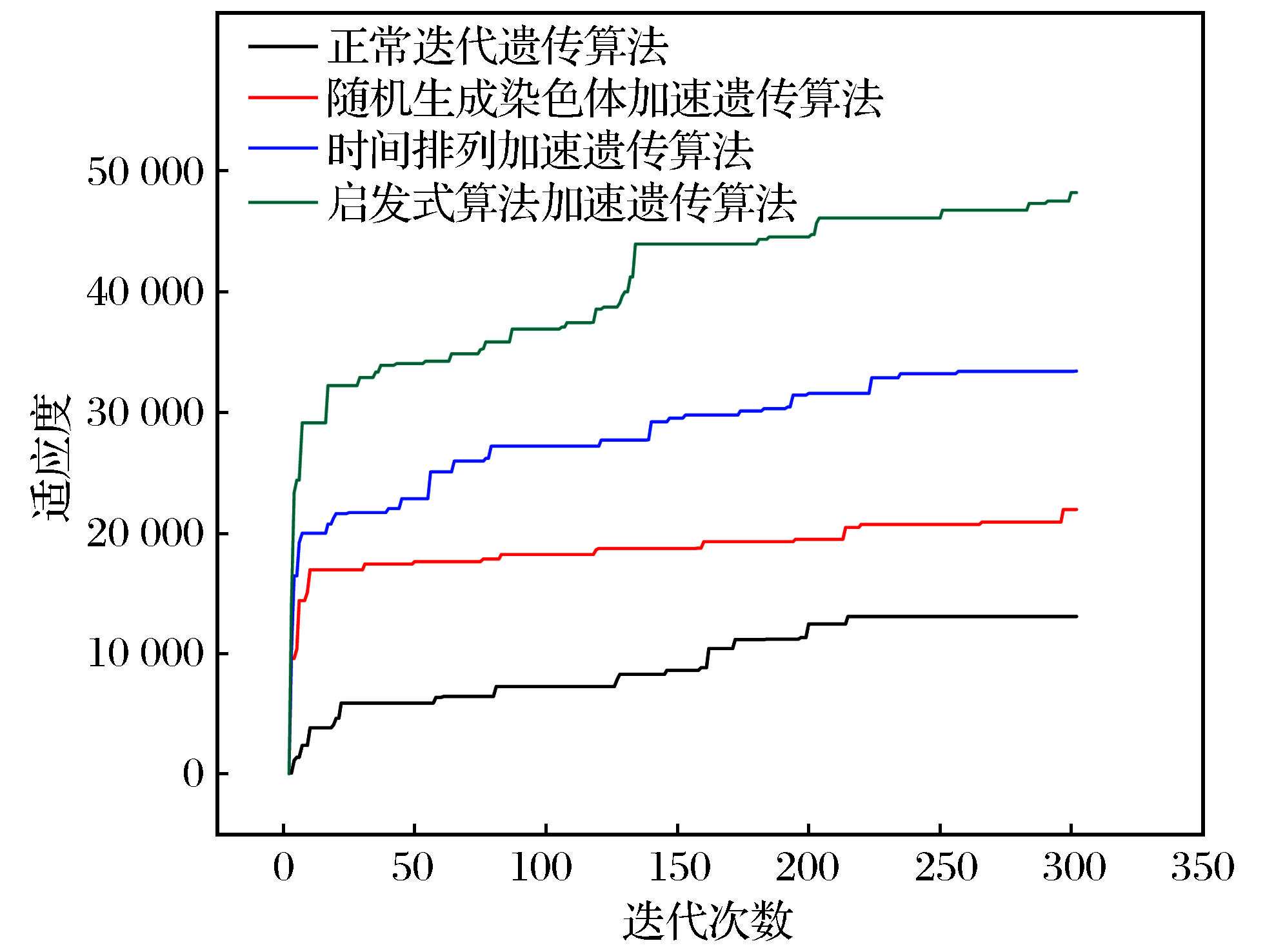
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |