浏阳市某采石场经过数年的地下开采,形成了由数个采空区形成的采空区群,部分采空区距离地表较近。同时,地表有正在运行的县际九溪公路。为了制定矿山下—步开采计划和保障上方公路安全运行,需要对采空区群和上覆公路的稳定性进行综合分析和评判。
采空区的形成会破坏原有围岩的应力平衡[1,2,3],在应力重分布过程中会引起围岩变形和地表沉降[4,5,6],对周围采场和地表构筑物的安全产生影响[7,8,9];在采空区群形成后,围岩应力和应变会产生复杂的时空非线性叠加[10,11,12],使得其稳定性分析不同于单个采空区。对于上覆公路的采空区群而言,公路荷载的存在会使得采空区的应力应变情况进一步复杂化,甚至引起采空区覆岩的二次活化[13],保证资源利用和地表建筑物的安全是此类工程的要求[14]。在采空区上部建(构)筑物分析方面,学者们从采空区稳定性出发,开展了地表沉陷预测及其对建筑物的危害评判,童立元等[15,16,17,18]分析了采空区与上覆公路相互作用机制、危害判别准则,总结了相应的治理措施;孙琦等[19]分析了浅埋煤矿采空区在公路动荷载和水耦合条件下对路基稳定性的影响;张普纲[20]利用数值模拟提出优化高速公路下采空区治理的方案;赵斌臣等[21]利用数值模拟分析了采空区上高等级公路变形历程和非均匀沉降;规范方面,有采空区上新建公路的指导规范[22]。
现有研究大多针对煤矿和高速公路,在复杂地形条件和采空区群赋存较不规则的条件下采空区与较低等级公路相互作用的研究有待丰富。本文基于实际矿山工程,利用FLAC3D软件模拟采石场采空区群和上覆公路稳定性情况,得出采空区和公路整体稳定、沉陷不均及局部离层的结论,针对性地提出了充填4#采空区的建议。
1 工程概况
采石场位于浏阳市城区西直线距离约16 km处,区域地貌为剥蚀丘陵,地形坡度在25°~35°之间。九溪公路从空区2上方及空区1与空区2交界处上方通过,空区顶板距离地表厚度为30~80 m。该矿山采用房柱式开采,生产规模为3×104 t。
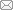
根据采空区的实际分布状况,进行了采空区测点布置,采空区分布及测点编号见图1。
图1
表1 采空区基本情况
Table 1
| 采空区编号 | 采宽/m | 采宽超幅/m | 采长/m | 空区面积/m2 | 采高/m | 采高超幅/m | 空区体积/m3 | 空区顶板距地表高度/m | 是否采完 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总计 | 4 520 | 44 120 | |||||||
| 空区1 | 14 | 4 | 100 | 1 400 | 13 | 3 | 18 200 | 40 | 是 |
| 空区2 | 10 | / | 200 | 2 000 | 8 | / | 16 000 | 80 | 否 |
| 空区3 | 8 | / | 40 | 320 | 6 | / | 1 920 | 85 | 是 |
| 空区4 | 10 | / | 80 | 800 | 10 | / | 8 000 | 90 | 否 |
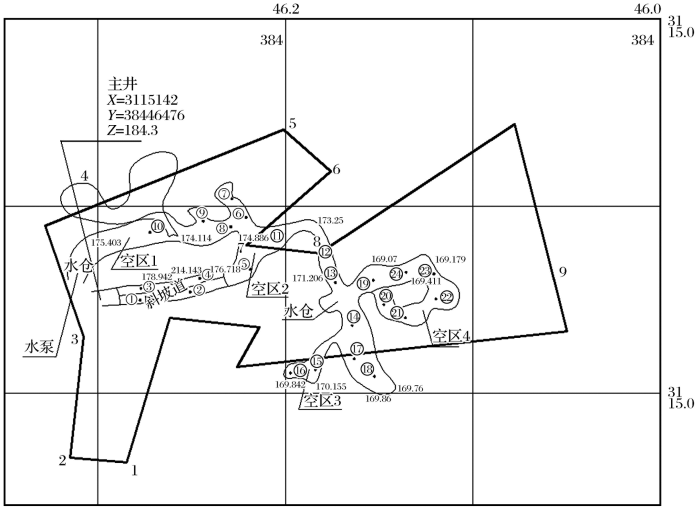
图2
图2
采空区与地表公路空间位置图
Fig.2
Spacial location map of goaf group and overlying highway
2 模拟参数
2.1 围岩物理力学参数
经现场调查,计算得到该矿山的石灰岩RQD=87.91、RMR=62、Q=115,质量等级为Ⅱ级,工程岩体岩石质量评价为良好岩体。
表2 岩石力学强度参数离散性分析结果
Table 2
| 统计项目 | Is/MPa | Is(50)/MPa | RC/MPa | Rt/MPa | C/MPa | Φ/(°) | E/MPa | v |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 统计总数 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 最大值 | 3.893 | 4.308 | 71.148 | 3.352 | 25.655 | 20.17 | 71 403.834 | 0.134 |
| 最小值 | 1.061 | 1.452 | 32.049 | 1.321 | 11.384 | 19.88 | 57 707.332 | 0.133 |
| 平均值 | 2.174 | 2.732 | 50.310 | 2.252 | 18.037 | 20.03 | 63 844.740 | 0.134 |
| 标准值 | 1.677 | 2.206 | 43.073 | 1.876 | 15.396 | 19.976 | 61 321.641 | 0.134 |
| 标准差 | 0.946 | 1.003 | 13.801 | 0.715 | 5.036 | 0.11 | 4 811.507 | 0.000 |
| 变异系数 | 0.435 | 0.367 | 0.274 | 0.318 | 0.279 | 0.01 | 0.075 | 0.003 |
| 统计修正系数 | 0.772 | 0.807 | 0.856 | 0.833 | 0.854 | 1.00 | 0.960 | 0.999 |
表3 室内岩石力学试验强度参数离散性统计
Table 3
| 统计项目 | ρ/(kN·m-3) | RC/MPa | Rt/MPa | E/MPa | v |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 统计总数 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 最大值 | 27.570 | 77.795 | 4.228 | 25.07 | 0.283 |
| 最小值 | 27.150 | 24.574 | 3.418 | 2.77 | 0.141 |
| 平均值 | 27.448 | 53.629 | 3.770 | 16.95 | 0.172 |
| 标准值 | 27.284 | 33.860 | 3.465 | 8.519 | 0.113 |
| 标准差 | 0.173 | 20.827 | 0.322 | 8.88 | 0.062 |
| 变异系数 | 0.006 | 0.388 | 0.085 | 0.52 | 0.362 |
| 统计修正系数 | 0.994 | 0.631 | 0.919 | 0.50 | 0.657 |
根据现场工程地质调查,计算得到石灰岩的地质强度指标(GSI)值为GSI=57,采用Heok-Brown准则及其强度参数的估计法,得到该矿山的岩体力学强度参数见表4。
表4 岩体力学强度参数
Table 4
| 参数 | 数值 | 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 抗压强度/MPa | 4.835 | 摩擦角/(o) | 34.15 |
| 抗拉强度/MPa | 0.215 | 弹性模量/GPa | 10.954 |
| 黏聚力/MPa | 3.145 |
2.2 公路参数及荷载
采空区上覆公路为三级普通混凝土公路,面层厚度为0.2 m,基层厚度为0.6 m,垫层厚度为1 m,路面设计基准期为20年。由于地形较为复杂,设计车速为30 km/h,安全等级为四级,变异水平等级为中—高级,考虑偏载、动载等因素下路面疲劳损坏的综合系数为1.10。
表5 网格组计算参数
Table 5
| 网格组 | 本构模型 | 弹性模量E | 泊松比 | 容重/(kN·m-3) | 内聚力/(kN·m-2) | 摩擦角/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 面层 | 摩尔库伦 | 1 GPa | 0.3 | 22 | 60 | 35 |
| 基层 | 摩尔库伦 | 500 MPa | 0.25 | 21 | 45 | 30 |
| 垫层 | 摩尔库伦 | 200 MPa | 0.3 | 20 | 30 | 25 |
| 表土 | 摩尔库伦 | 28 MPa | 0.3 | 19 | 17 | 22 |
| 矿石及围岩 | 摩尔库伦 | 10.95 GPa | 0.45 | 27.2 | 3 145 | 34.2 |
3 模拟结果
3.1 地表沉陷与采空区顶板下沉分析
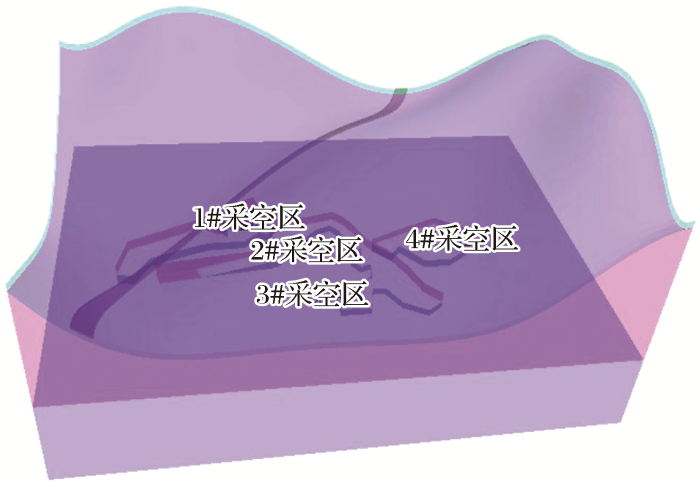
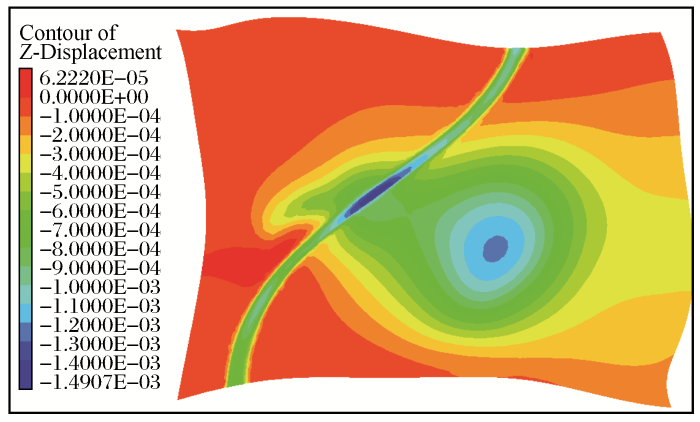
(1)地表沉陷分析。图3显示地表多数区域沉陷不足1 mm,最大沉陷量为1.49 mm。地表沉陷较大的区域分布在1#与2#采空区之间的矿柱附近,1#采空区正上方的公路,4#采空区及其周围矿柱正上方。在公路中段出现一个沉降中心区,沉降最大值即发生在此区域,该中心正下方是1#采空区,同时也压覆了1#与2#采空区之间的局部矿柱。从公路横向看,该沉降中心偏向2#、3#和4#采空区形成的采空区群。
图3
(2)公路荷载对地表沉陷的影响分析。在经历初始应力模拟、采空区形成模拟后,为探究行车荷载对采空区的影响,将第2.2小节选取的行车荷载以法向压力的形式施加于路面,随后计算至模型平衡。
图4
(3)采空区顶板下沉分析。图5显示4#采空区顶板下沉量最大,最大值达4.846 mm,大部分下沉超过2 mm,主要是4#采空区顶板中部大面积无矿柱支承,且其与2#采空区连接矿柱较薄;1#采空区顶板下沉最大值为1.5 mm;3#采空区和2#采空区贯通,在连通部分达到最大下沉量2.5 mm;2#采空区顶板沉陷相对较小。
图5
3.2 采空区应力场分析
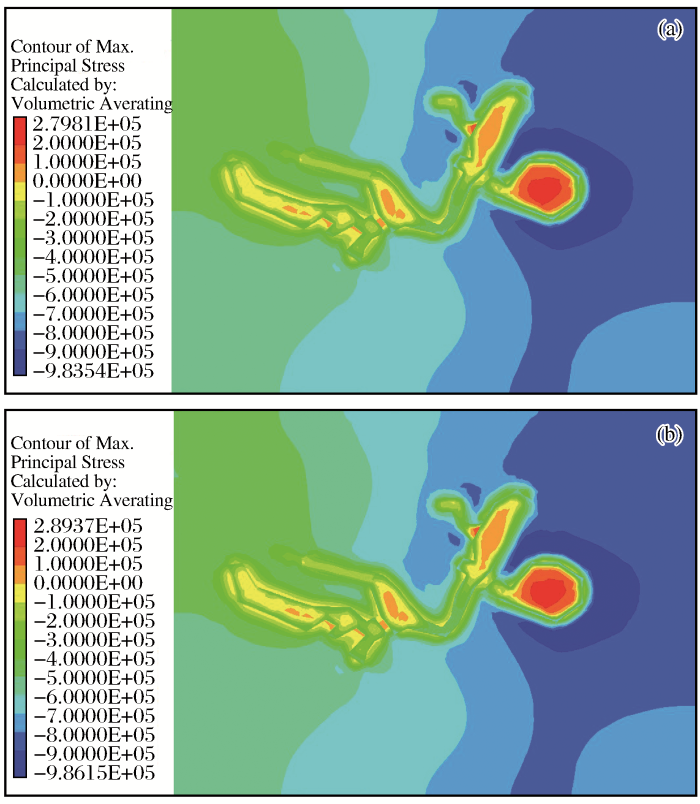
图6显示4#采空区顶板中央部分出现拉破坏,其他采空区未见拉破坏,在公路路面施加荷载后破坏区有小面积增加,但影响很小。
图6
图6
顶板最大主应力云图
Fig.6
Contour of maximum principal stress of uprock
(a)面荷载施加前顶板最大主应力;(b)面荷载施加后顶板最大主应力
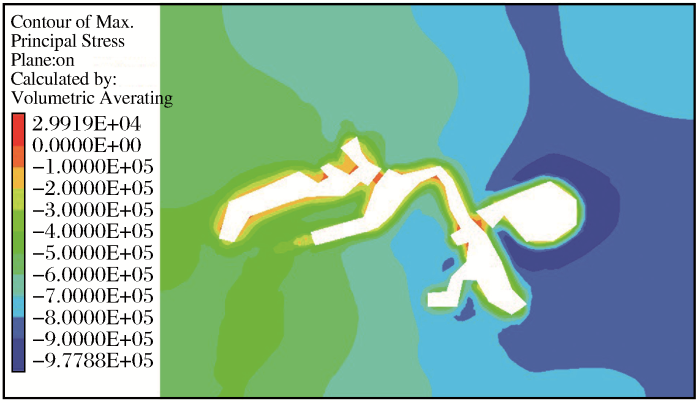
图7显示矿柱中上部的尖角矿柱处有拉压力集中,此外,在1#与2#采空区、3#与4#采空区之间的薄弱矿柱处也出现拉压力集中,其中有少部分区域拉应力超过围岩抗拉强度。
图7
图7
矿柱中等高度最大主应力云图
Fig.7
Contour of maximum principal stress in medium height of pillar
3.3 公路路面离层分析
实际观察发现地表公路面层出现离层现象,部分区域面层与基层脱离,为模拟离层破坏,在面层与基层之间设置接触面。
模拟结果表明,在数值计算过程中,离层首先出现在道路边缘,随后出现在路线中央。离层区分布呈现出整体较为分散,局部集中的特点;整体而言形成不均匀分布的局部条带状离层区域,如图8所示。
图8
从离层区域与采空区的相对空间位置来看,大部分道路边缘离层区域出现在靠近大面积采空区一侧,1#采空区部分在路线正下方,2#、3#和4#采空区在路线右侧;从地表地形来看,中央离层区域主要发生在公路上坡路段与洼地,而在较平坦的路段上离层区域分布密度很小。采空区群在路线两侧的不均匀分布导致了路面沉降的不均匀,同时上坡和洼地路段的公路的受力条件较之平坦路段较为不利,再加上采用的是均布面荷载代替公路荷载,而实际荷载多较集中地分布在靠近路线边缘侧,导致了路面的离层分布出现线条式集中和局部点片式离层特点。
4 结论
(1)采空区对于地表公路破坏有限,仅在4#采空区顶板及矿柱拐角处存在拉破坏。
(2)地表地形对采空区和公路稳定性的影响较大,采空区引起的不均匀沉降带来的沉陷曲率改变和局部离层对于公路的危害较大,并且采空区引起的地面沉降是一个长期的过程,其次生危害较严重,可对离层部分注浆加固。路面大荷载对于公路的影响是直接的,也可能引起采空区的二次活化,应尽量避免。
(3)综合公路路基沉陷与公路离层分析可知,公路与采空区的相对空间位置及公路路段所处的地表地形对公路的破坏形式起着主要控制作用,建议充填4#采空区。
参考文献
采空区下方高应力环境下深部矿体回采时序研究
[J].
Study on mining sequence of deep orebody under high stress environment below goaf
[J].
Calculation of stress-strain state for an over-goaf rock mass
[J].
Bayes discriminant analysis method to identify risky of complicated goaf in mines and its application
[J].
开采方案对地表移动影响的数值模拟
[J].
Numerical simulation of effect of mining scheme on ground movement
[J].
Analysis of surface subsidence mechanism and regularity under the influence of seism and fault
[J].
Ground subsidence observations and a modified influence function method for complete subsidence prediction
[J].
基于FLAC3D程序的采空区稳定性分析
[J].
FLAC3D-Based stability analysis of mined-out area
[J].
河流下伏采空区地表沉降规律及处治技术研究
[J].
Research on the surface subsidence regularity and treatment technique of goaf underlying river
[J].
山东望儿山金矿地表沉陷数值模拟研究
[J].
Numerical simulation of mining-induced subsidence in Wang’ershan gold mine,Shandong Province
[J].
金属矿山采空区群形成过程中围岩扰动规律研究
[J].
Study of disturbance law for wall rock while goaf group formation in metal mines
[J].
基于蠕变试验的浅埋空区群结构时变力学特性研究
[J].
Study on time-variant mechanics properties of shallow goaf group based on creep experiment
[J].
复杂空区群回采围岩破坏模式及区域并行研究
[J].
Parallel computing technologies for the failure mode and area of surrounding rock in complex goafs
[J].
高速公路下伏多层采空区地表沉陷数值模拟及预测研究
[D].
Numerical Simulation and Ground Subsidence Prediction for Multilayer Goafs Underlaying Highway
[D].
基于FLAC3D 的公路下压煤巷式充填开采的数值模拟分析
[J].
Simulation analysis of roadway backfilling mining under highway based on FlAC3D
[J].
高速公路与下伏煤矿采空区相互作用规律探讨
[J].
Discussion of interaction law of expressway and underlying mine goafs
[J].
高速公路下伏采空区问题国内外研究现状及进展
[J].
Current research state of problems associated with mined-out regions under expressway and future development
[J].
高速公路下伏采空区危害性评价与处治技术
[M].
Hazard Potential Evaluation and Treatment Technology of Highway Underlain Goaf
[M].
采空区对高速公路危害性特征与评价方法研究
[J].
Hazard characteristics and the evaluation methods for mined-out region under expressways
[J].
浅埋采空区对路基稳定性影响的数值模拟
[J].
Numerical simulation of the impact of shallow seam goaf on highway safety
[J].
采空区高速公路路基破坏的数值模拟分析
[J].
Numerical simulation of expressway roadbed over mined gob
[J].
高等级公路采动变性破坏数值模拟研究
[J].
Numerical simulation study on high-class failure due to mining deformation
[J].
《采空区公路设计与施工技术细则》的解释与应用
[J].
Interpretation and application of Techinicals for Design and Construction of Mined-out Area Highway
[J].




 甘公网安备 62010202000672号
甘公网安备 62010202000672号